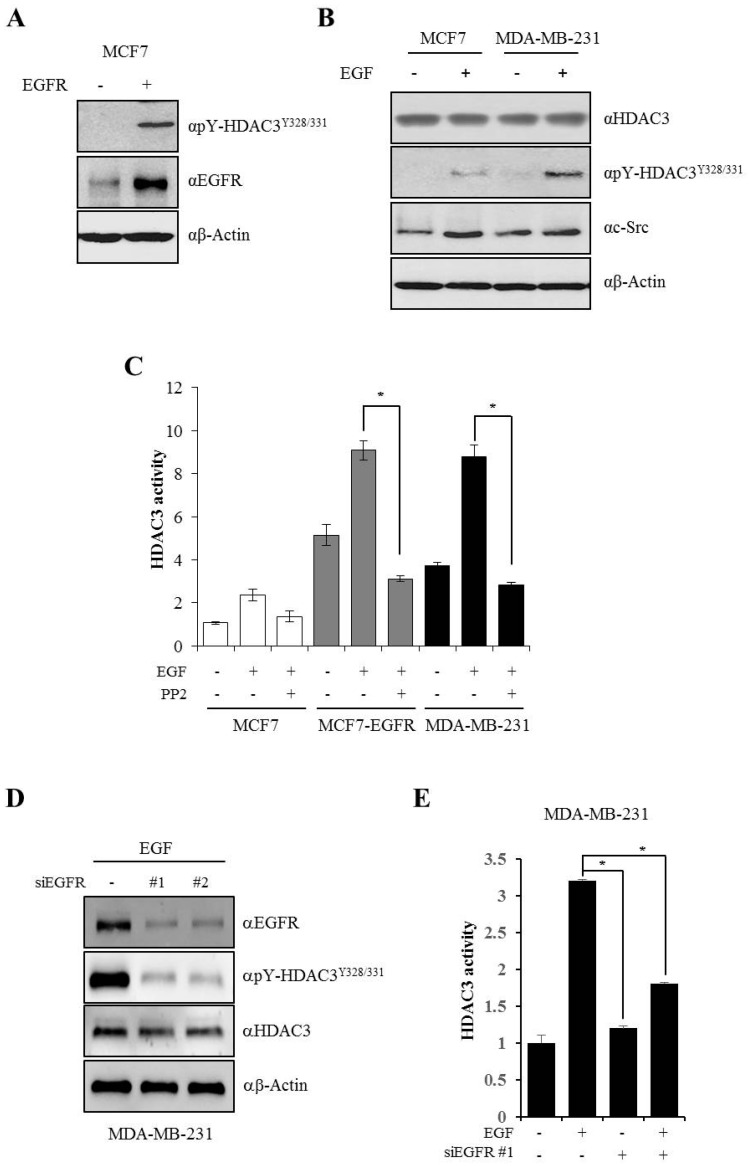
Figure 4.
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of HDAC3 is dependent on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). (A) EGFR is essential for the phosphorylation of HDAC3. EGFR was transfected into MCF7 cells, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with indicated antibodies. (B) EGF-induced HDAC3 phosphorylation is dependent on EGFR. MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with EGF, and cell lysates were analyzed with indicated antibodies. (C) The activation of EGFR signaling is critical for HDAC3 enzymatic activity. Various breast cancer cells were treated with EGF with/without PP2. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC3 antibody and assayed for histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. (D) The phosphorylation of HDAC3Y328/331 is dependent on the EGFR signaling pathway. Phosphor-HDAC3Y328/331 was observed by Western blotting after EGFR knockdown under the indicated condition in MDA-MB-231 cells. (E) HDAC3 activity is dependent on EGFR. Small interfering RNA against EGFR (siEGFR) was transfected, and EGF was treated for 20 min before harvest. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC3 antibody and assayed for HDAC activity. Results are expressed as fold changes in OD values relative to OD values of control. The values presented are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05.