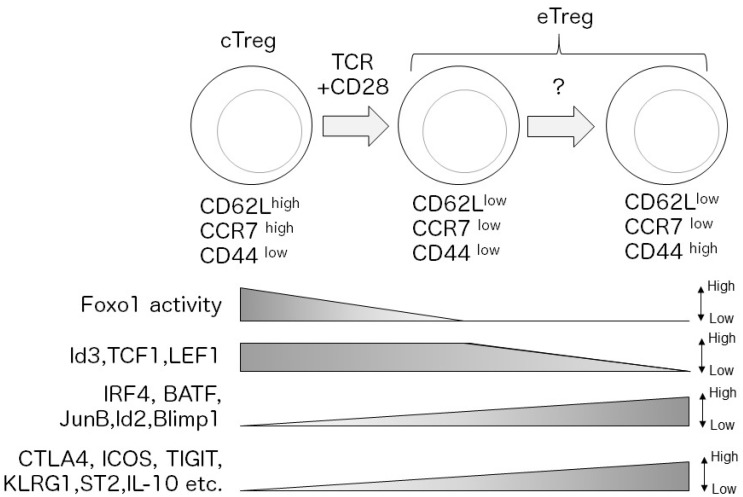
Figure 1.
Upon antigen stimulation, central Treg (cTreg) cells (CD62Lhi CCR7hi CD44lo) differentiate into effector Treg (eTreg) cells (CD62Llo CCR7lo CD44hi) depending on TCR and CD28 signaling. After activation, TCR-dependent transcription factors, such as interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), are induced and regulate the eTreg transcriptional program. In contrast, Foxo1 is inactivated by Akt-signaling, which decreases expression of cTreg-related molecules. Loss of Id2, transcription factor 1 (TCF1), and lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF1) expression is a signature of mature eTreg cells. Mature eTreg cells highly express immune suppressive molecules, such as cytotoxic T cell antigen 4 (CTLA4) and inducible T cell costimulator (ICOS).