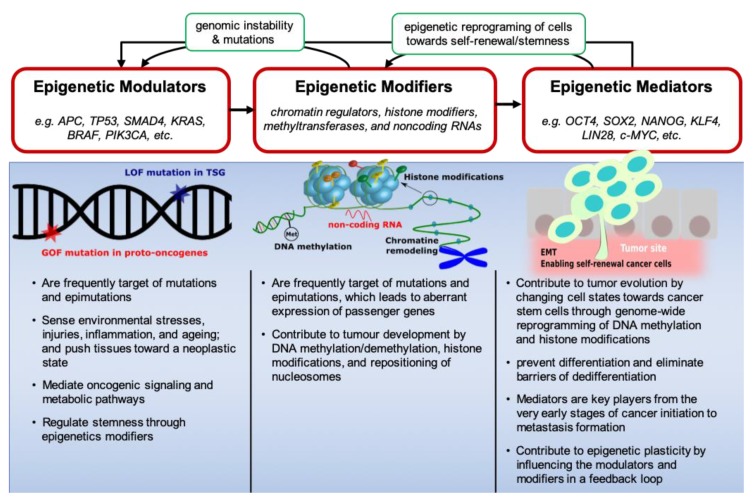
Figure 1.
Epigenetic functional system in the initiation and progression of CRC. Environmental cues, such as repeated exposure to carcinogens, inflammation, injury, and ageing impinge on epigenetic modulators. These, in turn, destabilize the epigenome through signalling and metabolic pathways. As a result, chromatin states at epigenetic mediator genes are changed triggering their unscheduled expression. Epigenetic mediators can also influence the plasticity of tumour cells during neoplasia, giving rise to the formation of CSCs and metastases. In all these processes, epigenetic modifiers play a central role. Mutations are frequently seen in epigenome modifying genes and, conversely, the epigenetic changes can cause further mutations and genomic instability in modulators. LOF = loss of function; TSG = tumour suppressor gene; GOF = gene of interest; Met = methylation; EMT = epithelial to mesenchymal transition.