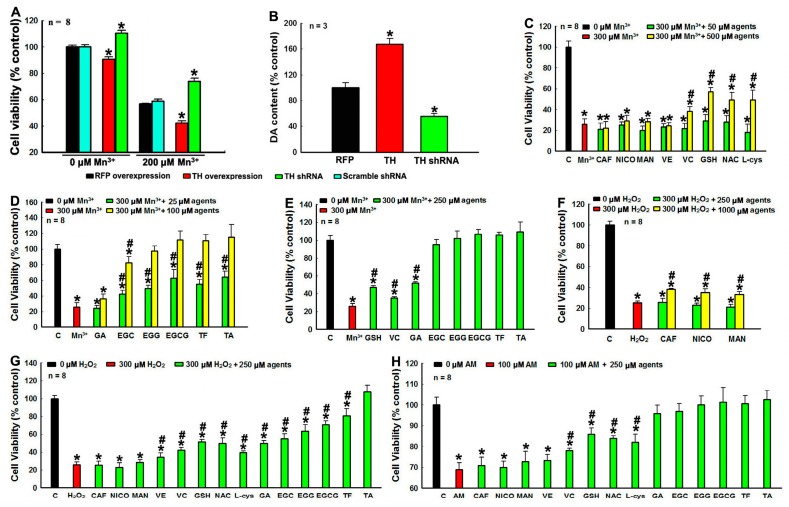
Figure 5.
Protection against Mn3+, H2O2, and AM induced dopaminergic PC12 cell death by tea polyphenols and other agents. Dopaminergic PC12 cells were challenges with 200 or 300 μM Mn3+ or 300 μM H2O2 overnight or 100 μM AM 3 h respectively in the presence or absence of various agents. Cells without any challenges are set as control. *, at least p < 0.05, compared with cell viability of control cells. #, at least p < 0.05, compared with cell viability of cells challenged with stressors only. (A,B), The Mn3+ induced cell toxicity are dependent on endogenous DA level in PC12 cells. (A) Influence on PC12 cell viability by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) overexpression or knockdown under Mn3+ overnight challenge. PC12 cells were transfected with rat-TH or TH shRNA vectors overnight respectively, before subsequent 200 μM Mn3+ overnight challenge. (B) Influence on DA level in PC12 cells by TH overexpression or knockdown. (C–E) Protection of PC12 cells against 300 μM Mn3+ overnight challenges induced toxicity by different agents. (C) Protection by 50 and 500 μM CAF, NICO, MAN, VE, VC, GSH, and l-cys. (D) Protection by 25 and 100 μM GA, EGC, EGCG, TF, and TA. (E) Protection by 250 μM GSH, l-cys and tea polyphenols. (F–H), protection against 300 μM H2O2 or 100 μM AM challenges induced toxicity by various agents. (F) Protection against H2O2 induced toxicity by 250 and 1000 μM CAF, NICO, and MAN. (G) Protection against H2O2 induced toxicity by 250 μM agents. (H) Protection against 100 μM AM induced toxicity by 250 μM agents.