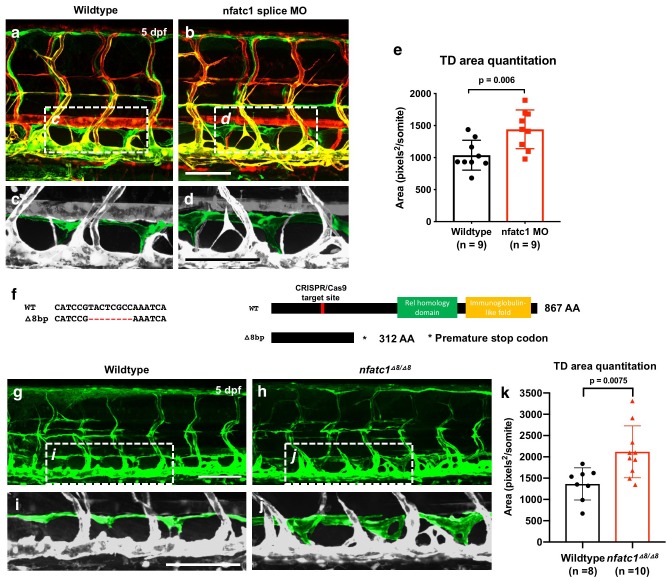
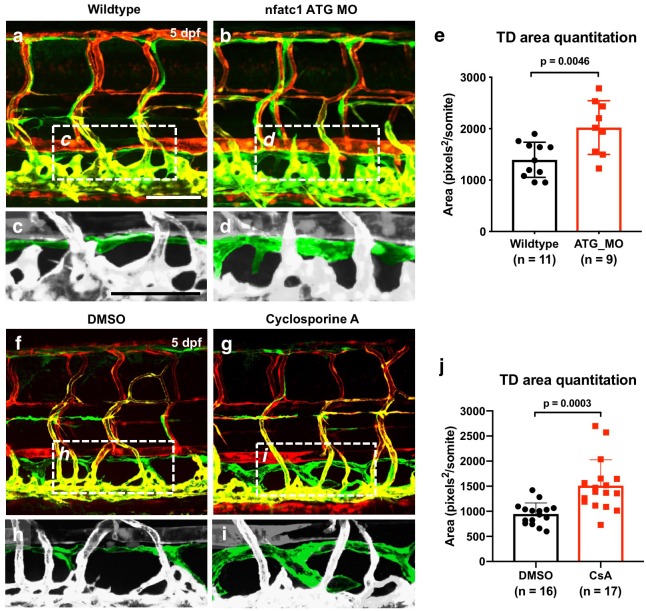
Figure 6. Suppression of Nfatc1 promotes enlargement of the thoracic duct.
(a,b) Confocal images of the mid-trunk of 5 dpf Tg(mrc1a:eGFP)y251, Tg(kdrl:mCherry)y171 double-transgenic control MO (a) or nfatc1 splice MO (b) injected animals. The dashed boxes in panels a and b show the areas magnified in panels c and d, respectively. (c,d) Magnified images from panels a and b, with the thoracic duct pseudocolored in green and other vessels in gray. (e) Quantitation of thoracic duct size measured as the area encompassed by the thoracic duct in confocal images of the same seven mid-trunk somitic segments in five dpf wildtype (n = 9) and nfatc1 MO-injected (n = 9) animals. (f) Sequence alignment of wildtype and nfatc1△8/△8 mutant genomic DNA. Schematic of nfatc1 protein domains, CRISPR target site, and truncated mutant nfatc1 polypeptides. (g,h) Confocal images of the mid-trunk of 5 dpf Tg(mrc1a:eGFP)y251 wildtype (g) or nfatc1△8/△8 mutant (h) animals. (i,j) Magnified images from panels g and h, with the thoracic duct pseudocolored in green and other vessels in gray. (k) Quantitation of thoracic duct size measured as the area encompassed by the thoracic duct in confocal images of the same seven mid-trunk somitic segments in five dpf wildtype (n = 8) and nfatc1△8/△8 mutant (n = 10) animals. Rostral is to the left in all images. Scale bar = 100 μm (b,d,g,i). All graphs are analyzed by t-test and the mean ± SD is shown.