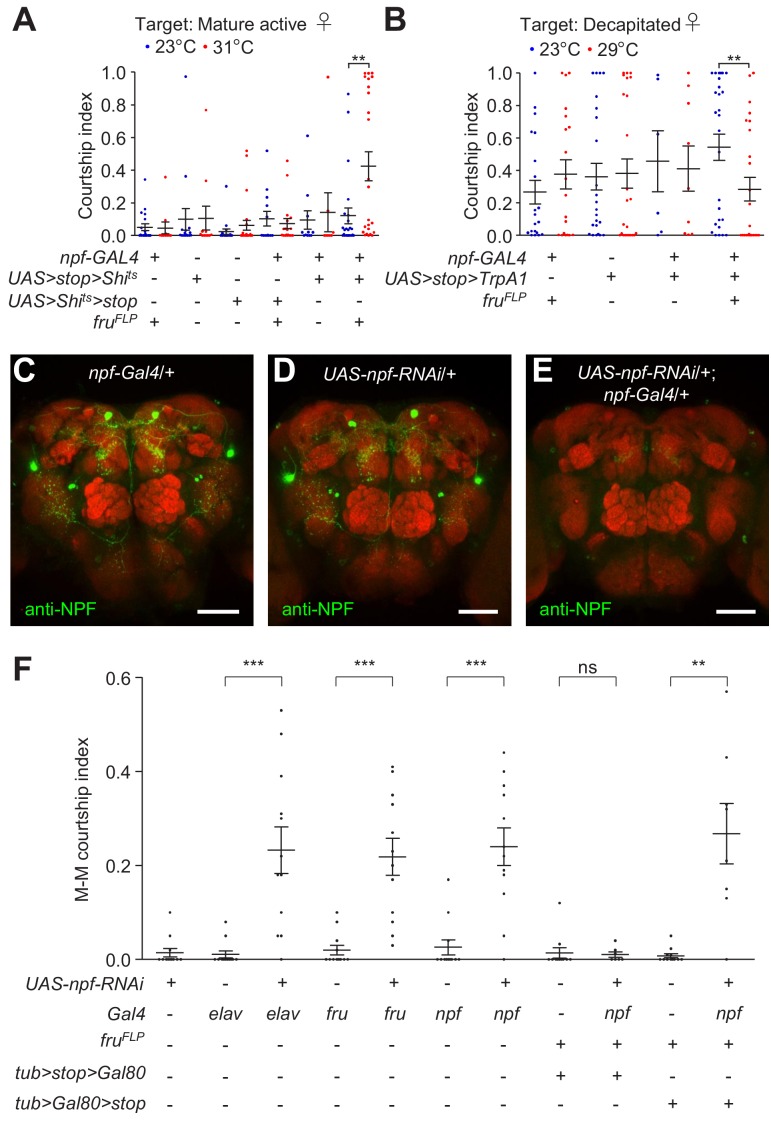
Figure 4. Specificity of NPFM neurons in regulating male courtship.
(A) Single tester males of the indicated genotypes were assayed for male-female (M–F) courtship at both permissive (23°C) and non-permissive (31°C) temperatures for Shits. Newly-eclosed male flies were isolated for 5 days, after which they were housed with 5—7 w1118 virgin female flies for 4 hr prior to the experiment. 7—15 day-old mature active mated w1118 female flies were used as targets. The courtship index is the mean ratio of time spent by the tester male in courtship within 30 min following a 10 min incubation period. n = 8—24. Bars indicate means ± SEMs. Significance was determined using Mann-Whitney test. **p < 0.01. (B) Single tester males of the indicated genotypes were assayed for courtship at two different temperatures (23°C and 29°C). Newly-eclosed males that were isolated for 2 days were used as testers. Decapitated w1118 female flies were used as the targets. Courtship index represents the mean ratio of time the male flies spent in courting within 10 min following a 5 min incubation period. n = 6—27. Bars indicate means ± SEMs. Significance was determined using Mann-Whitney test. **p < 0.01. (C—E) Immunohistochemistry showing the effect of npf RNAi knock down on NPF protein expression in male brains. Control genotypes of npf-Gal4/+ and UAS-npf-RNAi male brains and experimental genotype of npf-Gal4/+;UAS-npf-RNAi/+ male brains were immuno-stained with anti-NPF. Scale bars indicate 50 μm. (F) Effects on male-male (M–M) courtship due to RNAi knock down of npf in all neurons (elav), fru neurons, npf neurons, non-NPFM npf neurons and NPFM neurons. n = 7—12. The bars indicate means ± SEMs. Mann-Whitney test was used to determine significance. **p < 0.01.