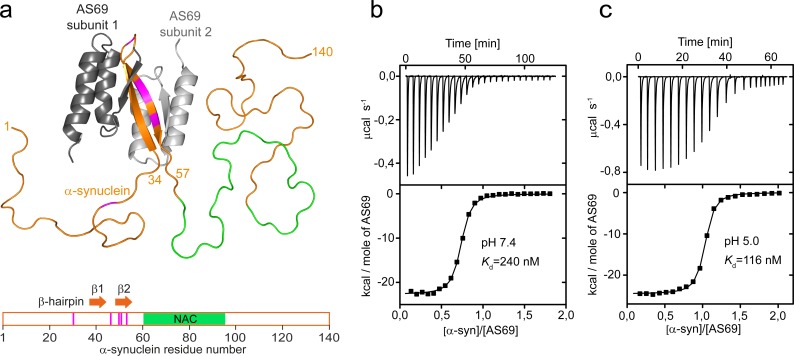
Figure 1. AS69 binds to monomeric -synuclein, inducing local folding of the region comprising residues 37–54 into a -hairpin conformation.
(a) Structural model of the AS69:-synuclein complex based on NMR (pdb entry 4BXL) (Mirecka et al., 2014), generated with PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, 1.2; Schrödinger, LLC.). AS69 (grey) is a disulfide-linked homodimer. -Synuclein (orange) locally adopts -hairpin conformation, while the remainder of the molecule, including the hydrophobic NAC segment (green), remains intrinsically disordered (Mirecka et al., 2014). Positions at which disease-related mutations have been identified are given in magenta. (b,c) The affinity of AS69 to -synuclein at pH 7.4 (b) and pH 5.0 (c) analyzed by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) experiments. Titration of 420 μM -synuclein into 47 μM AS69 in 20 mM sodium phosphate, 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.4 (b), or 320 μM -synuclein into 32 μM AS69 in 20 mM sodium acetate, pH 5.0 (c), at 30 °C. The upper panels show the baseline-corrected instrumental response. The lower panels show the integrated data (filled squares) and the fit to a 1:1 binding model (continuous line).