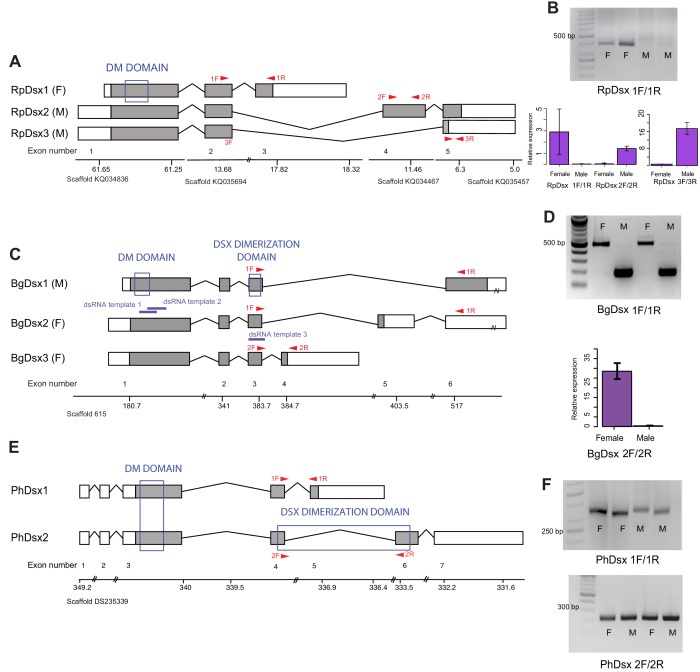
Figure 2. Doublesex shows sex-specific splicing in some but not all hemimetabolous insects.
Schematics showing doublesex transcripts isolated from Rhodnius prolixus, Blattella germanica, and Pediculus humanus. Coding sequences are in gray and UTRs in white. Sex-specificity of each transcript is noted in parentheses at the end of the transcript name. Transcripts are shown mapped to genomic scaffolds; double bars show breaks in scale. Functional domains are labeled and indicated by blue boxes. (A) Three dsx transcripts isolated from R. prolixus span multiple genomic scaffolds. RpDsx1 was isolated from 3’ and 5’ RACE libraries made from female RNA; RpDsx2 and RpDsx3 were cloned from RACE libraries synthesized from male RNA. (B) Top panel: RT-PCR showing female-specificity of RpDsx1, using primers in exons 2 and 3, as indicated with red arrows in (A). Bottom panel: qPCR showing female-specific expression of RpDsx1, and male-specific expression of RpDsx2 and RpDsx3, using primers indicated with red arrows in (A). Forward primer 3F spanned the exon 2/5 junction. (C) Three dsx transcripts isolated by 3’ and 5’ RACE and PacBio Isosequencing from B. germanica. The 3’ UTR of BgDsx1 and BgDsx2 contains a retrotransposon (marked with a break) and cannot be mapped to a single scaffold of the roach genome. Purple lines show the locations of dsRNA used for RNAi. Red arrows show primer locations for RT-PCR and qPCR. (D) Sex-specific expression of BgDsx isoforms. Top panel, PCR on cDNA of adult male and female fat body and reproductive tract with primers in exons 3 and 6. The larger band found exclusively in females contains the alternatively included exon 5, as confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Bottom panel, qPCR for exon 3/4 junction shows amplification only in females. (E) Two dsx transcripts isolated by 3’ and 5’ RACE from P. humanus male and female samples. (F) RT-PCR shows the presence of both PhDsx transcripts in both sexes.