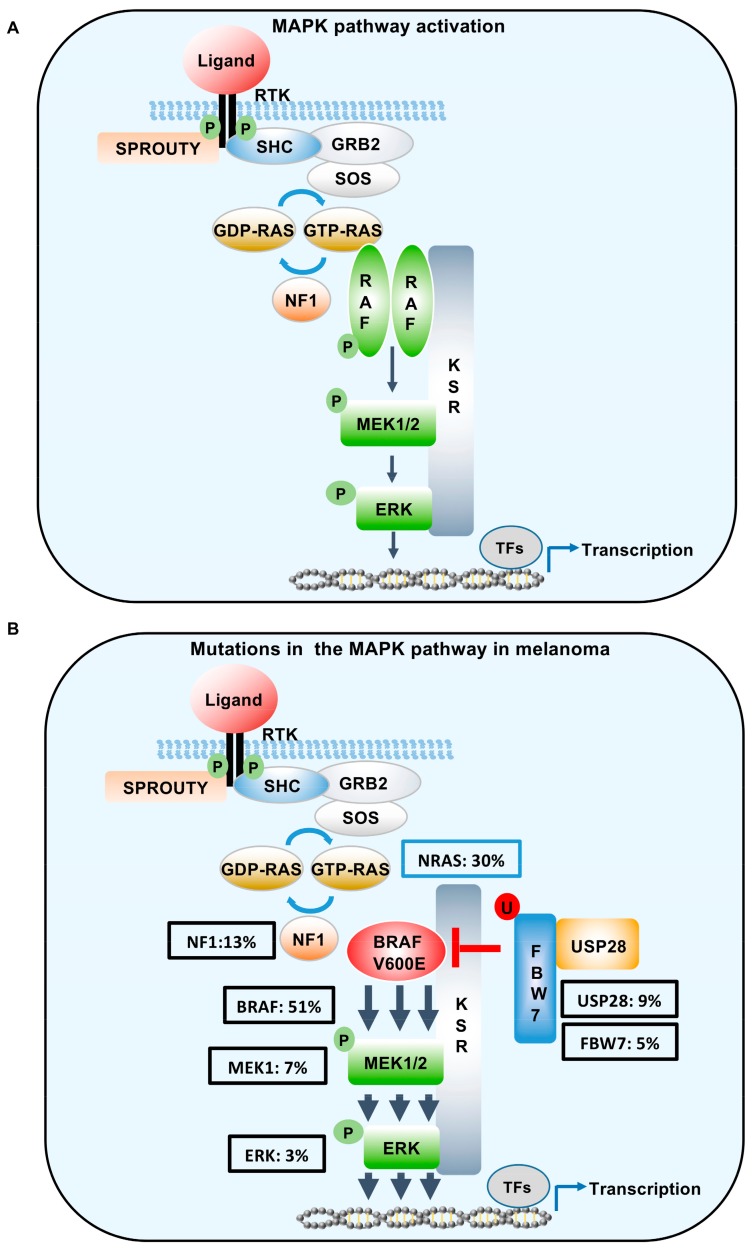
Figure 2.
Schematic of MAPK signalling in the context of wild type BRAF and mutant BRAFV600E. (A) In cells expressing wild type BRAF, ligand-induced activation of RTKs enhances RAS-GTP activity resulting in the dimerization and activation of RAF family members. This binding serves to phosphorylate MEK1/2, which then phosphorylates ERK, resulting in ERK-mediated transcription. (B) Hyper-activation of the pathway in melanoma can occur through oncogenic mutations in NRAS, BRAF, MEK1, ERK, or the loss of function mutations in NF1, FBW7, and USP28. Class I BRAF mutations (V600E) function as monomers to engage the MEK/ERK signal cascade. Mutation statistics were extrapolated from cBioPortal [30]. SHC, SHC adaptor protein 1; GRB2, growth factor receptor bound protein 2; SOS, son of sevenless; RAS, RAS proto-oncogene; NF1, neurofibromatosis 1; FBW7, F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7; USP28, Ubiquitin specific protease 28; TF, transcription factors; MAPK: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; BRAF: v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B; RTK: receptor tyrosine kinase; RAF: proto oncogene; MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: extracellular signal-related kinase.