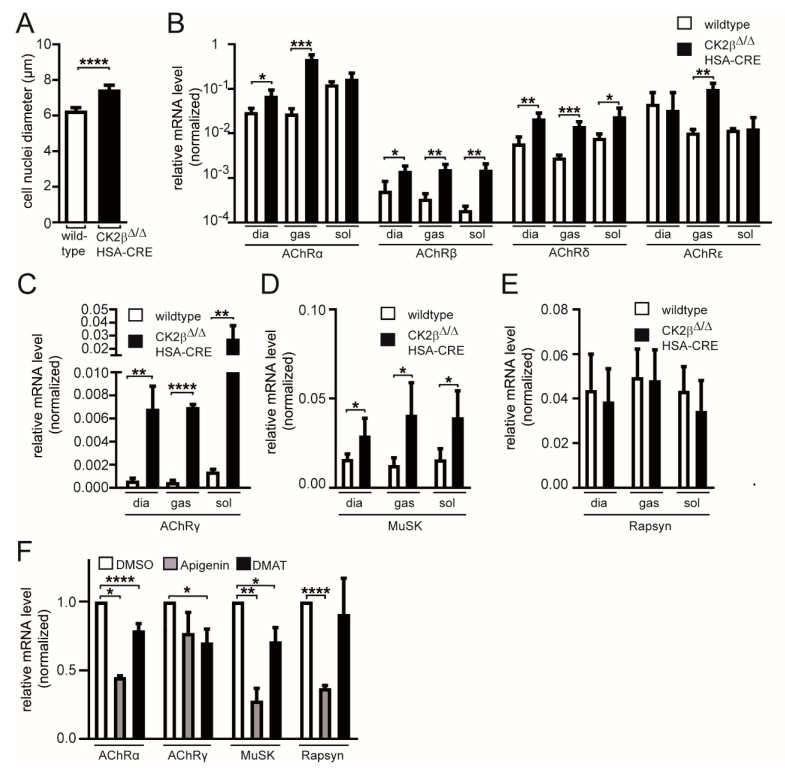
Figure 6.
Gene expression levels for postsynaptic genes in the absence of CK2β. (A) Analysis of cell nuclei diameter in soleus muscle of wild-type and conditional CK2β-deficient mice. Analyzed cell nuclei were significantly bigger in diameter in CK2β-deficient muscles when compared to wild-type cell nuclei (**** p < 0.0001; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; soleus wild-type; n > 50 cell nuclei, CK2β-deficient soleus n > 50 cell nuclei). Cell nuclei were sampled from three mice per genotype. (B–E) Relative transcript levels for AChRα, AChRβ, AChRδ, AChRε (B), AChRγ (C), MuSK (D), and Rapsyn (E) in diaphragm, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscle, as determined by quantitative PCR. Relative transcript levels of AChRβ, AChRδ (B), AChRγ (C), and MuSK (D) were significantly elevated in diaphragm, soleus, and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) (***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; n > 3 muscles per genotype). (F) After incubation of C2C12 muscle cells with common CK2 inhibitors Apigenin and DMAT, the transcript levels of typical postsynaptic genes were significantly reduced (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; n = 3 cell sets).