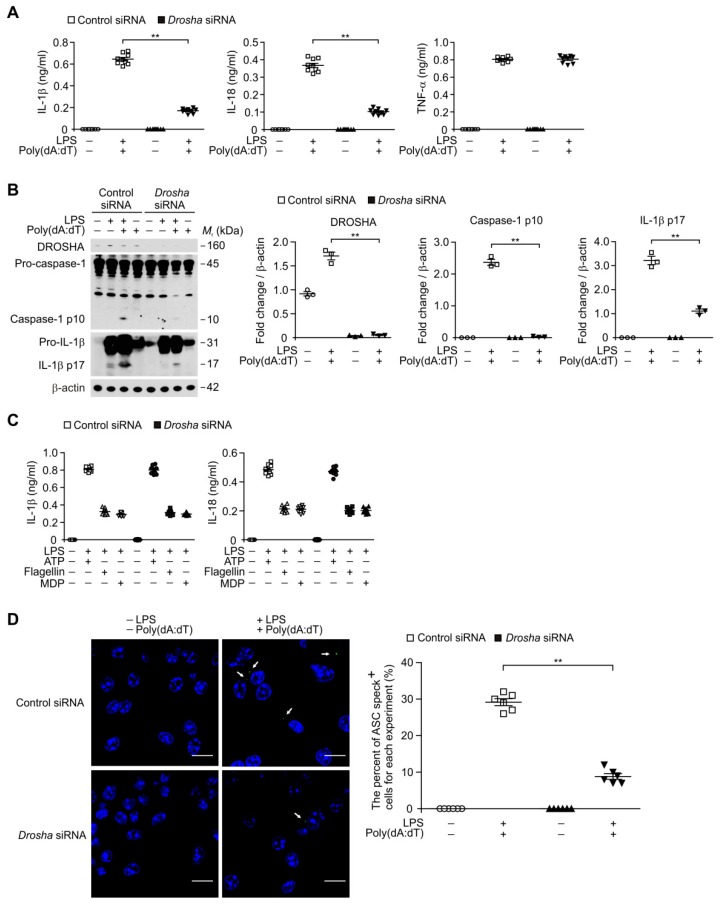
Figure 5.
Deficiency of DROSHA suppresses AIM2 inflammasome activation in macrophages. (A) Quantification of IL-1β (left), IL-18 (middle) and TNF-α (right) secretion from WT bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) transduced with DROSHA -targeting small interfering RNA (Drosha siRNA), or with a control plasmid (Control), and stimulated with LPS and poly(dA:dT) (n = 9 mice per group). (B) Representative immunoblot analysis for caspase-1 and IL-1β (left) and densitometry quantification of caspase-1 p10 and IL-1β p17 levels (normalized to levels of β-actin) (right) from WT BMDMs transduced with DROSHA -targeting siRNA (Drosha siRNA), or with a control plasmid (Control), and stimulated with LPS and poly(dA:dT). For immunoblots, β-actin was used as loading control (n = 3 mice per group). (C) Quantification of IL-1β and IL-18 secretion from WT BMDMs transduced with DROSHA -targeting siRNA (Drosha siRNA), or with a control plasmid (Control), and stimulated with LPS and either ATP, flagellin, or MDP (n = 9 mice per group). (D) Representative immunofluorescence images (total 100 cells in 10 individual images per group) (left) and quantification (right) of ASC speck formation (white arrows) (the number of ASC speck positive cells in 10 individual images per group) in WT BMDMs transduced with DROSHA -targeting siRNA (Drosha siRNA), or with a control plasmid (Control), and stimulated with LPS and poly(dA:dT). (n = 6 mice per group). Scale bars, 20 μm. Data are mean ± SEM. ** p <0.01; by Student’s two-tailed t-test or ANOVA.