FIG. 1. Amino acid models of the rat CCKAR and the rat CCKBR illustrating the receptor mutations.
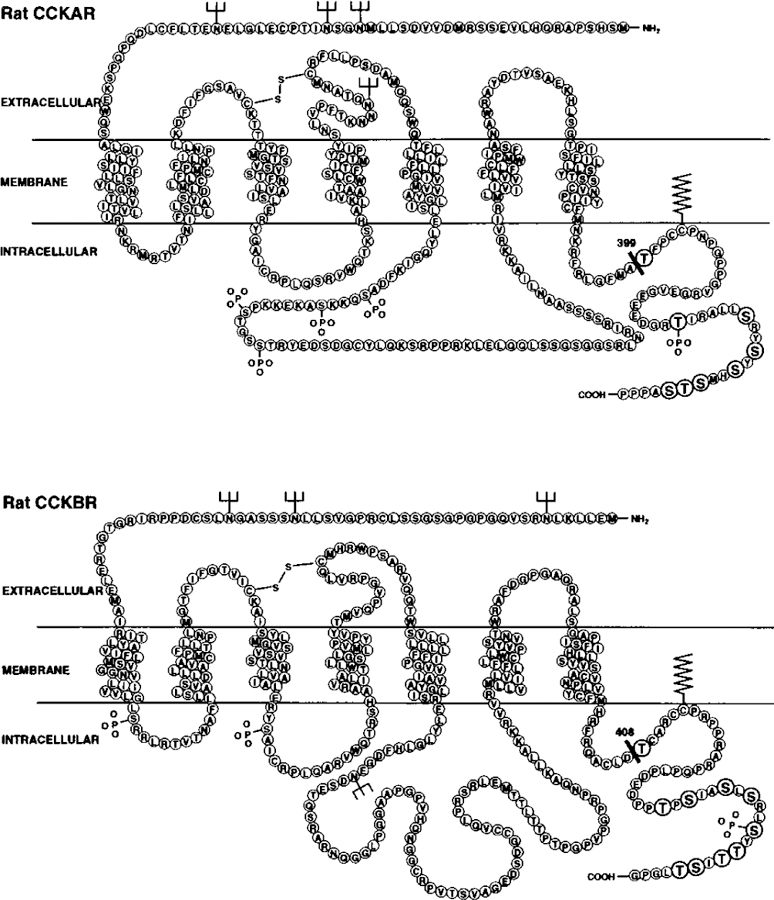
The models show the predicted amino acid sequence of the WT CCKAR (upper panel) and the WT CCKBR (lower panel). The mutant CCKAR Tr399 was constructed by truncation of the carboxyl terminus after amino acid residue 399, as indicated by the black bar. The mutant CCKAR ΔS/T was constructed by mutation of all eight serine and threonine residues in the carboxyl terminus (indicated by the enlarged and embolded circles) to alanines. In parallel, the mutant CCKBR Tr408 was constructed by truncation of the carboxyl terminus after amino acid residue 408 as indicated by the black bar. The mutant CCKBR ΔS/T was constructed by mutation of all 10 serine and threonine residues in the carboxyl terminus (indicated by the enlarged and embolded circles) to alanines.
