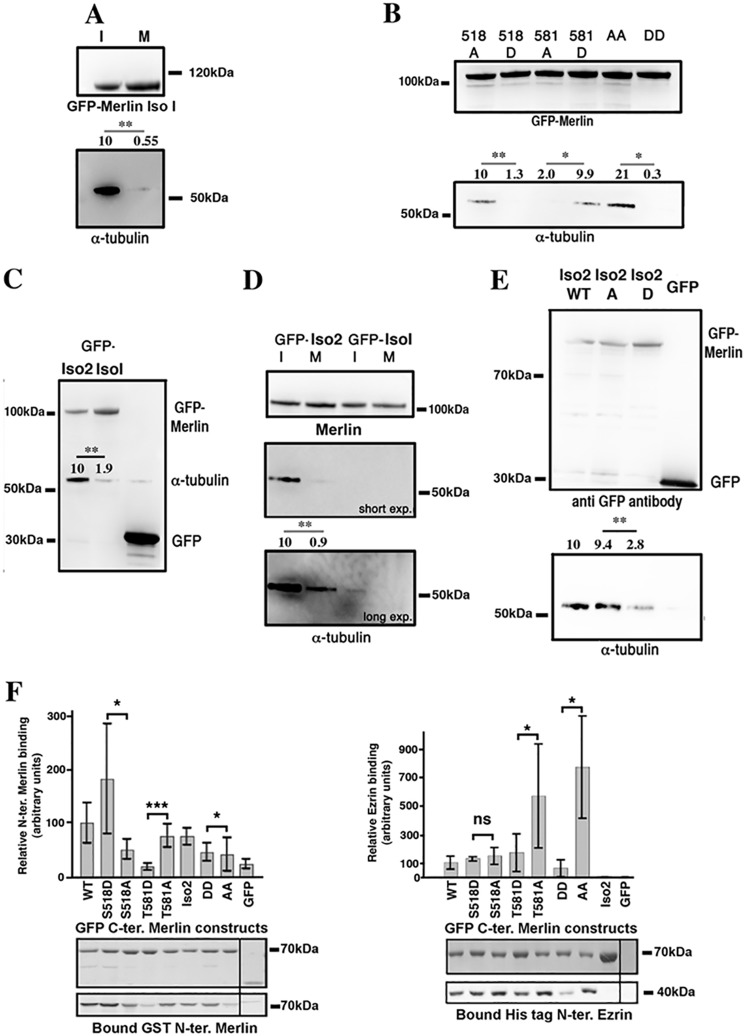
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation of Merlin modulate its interaction with α-tubulin and with ezrin. A, in HeLa cells, α-tubulin coprecipitates with GFP-Merlin isoform 1 from interphasic extracts (I) but much less from mitotic extracts (M). B, coprecipitation from interphasic HeLa cell extracts shows that S518D substitution prevents α-tubulin interaction. In contrast, T581D substitution promotes the interaction. Double AA and DD mutants coprecipitation experiments show that Ser-518 substitution is dominant over Thr-581. C, Merlin isoform 2 (Iso2) interacts more strongly with α-tubulin than isoform 1 (Iso1) in HeLa interphasic extracts. D, as observed for Merlin isoform 1, GFP-Merlin isoform 2 binding to α-tubulin strongly decreases during mitosis but the overall binding is higher than for isoform 1. E, S518D substitution inhibits Merlin isoform 2 interaction with α-tubulin assessed by co-immunoprecipitation from HeLa interphasic extracts. Average relative α-tubulin binding from at least three experiments is indicated. F, S518D substitution stimulates the binding of GFP-C-terminal. Merlin (330–595) isoform 1 to purified GST N-terminal Merlin (1–330). T581D substitution inhibits the interaction compared with T581A substitution. AA and DD C-terminal Merlin show minimal difference in binding to N-terminal Merlin (left panel). Remarkably, the alanine mutation of Thr-581 greatly facilitates the binding of the C-terminal half of Merlin fused to GFP to the His-tagged FERM domain of ezrin, when compared with the T581D substitution. The binding is even stronger when Ser-518 is also mutated to an alanine (AA) (right panel). The blot shows the quantity of bait protein used (GFP constructs) and the amount of interacting Merlin or ezrin N-terminal protein precipitated. All experiments were repeated at least three independent times. Student's t test; ns, p > 0.05; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. GFP was used as a control.