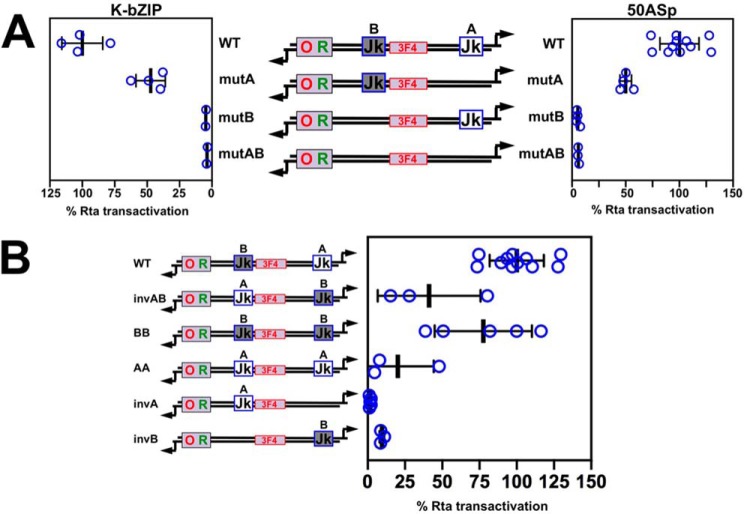
Figure 10.
RBP-Jκ element location is important for Rta transactivation of the ORF50AS and K-bZIP promoters. A, transactivation of the WT and mutant ORF50AS and K-bZIP promoters. Each RBP-Jκ–binding site in the promoter was mutated alone, or together, and then tested for Rta transactivation using the approach described in the legend to Fig. 7, A and B. Thick lines indicate means of values, and thin lines indicate standard errors. B, distance of the RBP-Jκ motif to the Rta-c/Oct-v motif determines Rta transactivation magnitude. Each RBP-Jκ–binding site in the promoter was altered as shown in the schematic and then tested for Rta transactivation using the approach described in the legend to Fig. 7, A and B. For both panels, results are shown as percentage of transactivation of WT promoters by Rta divided by empty vector. Promoter schematics follow the design described in the legend to Fig. 6. Thick lines indicate means of values, and thin lines indicate standard errors.