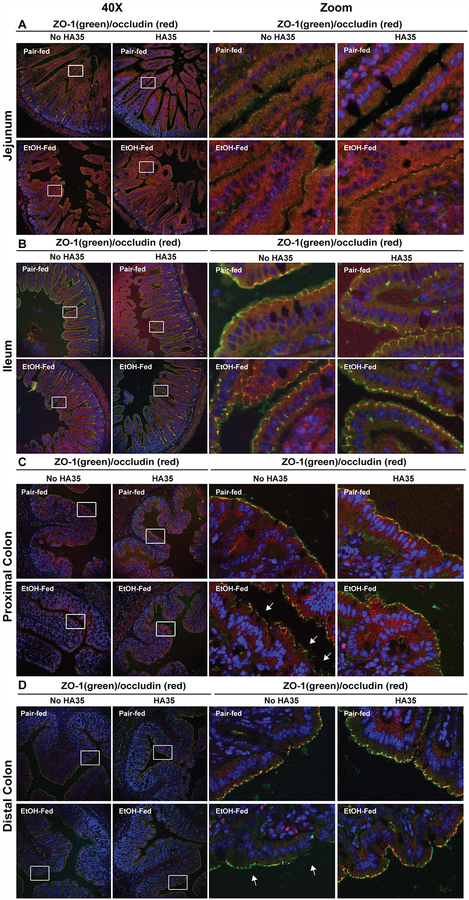
Figure 2: HA35 treatment prevented the short-term ethanol-induced disruption of ZO-1 and occludin co-localization at tight junctions in proximal and distal colon.
C57BL/6J mice were allowed free access to an ethanol containing diet (2 days at 11% of calories as ethanol then 2 days at 32% of calories as ethanol) or pair-fed an isocaloric control diet. Mice were provided with 15mg/kg body weight HA35 or an equivalent volume of saline by gavage during the last three days of the short-term ethanol feeding protocol. Immunostaining for ZO-1 (green) and occludin (red) in deparaffinized sections of (A) jejunum, (B) ileum, (C) proximal colon and (D) distal colon fixed with HistoChoice. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue) staining. Images were acquired at 40X magnification and are representative of duplicate images captured from n=4 pair-fed or n=6 ethanol-fed mice in each treatment group. White boxes indicate representative areas of tight junctions for each intestinal region that were digitally magnified for improved visibility.