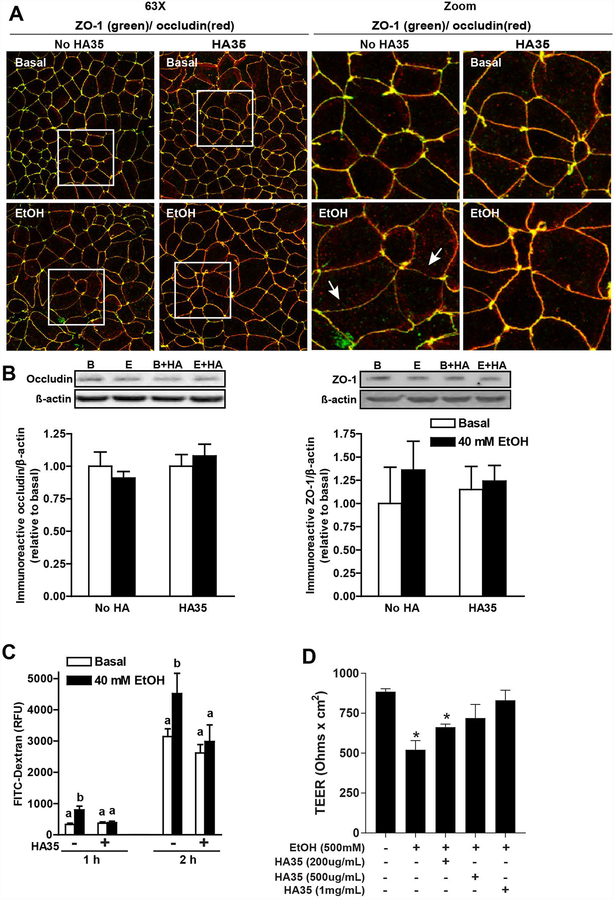
Figure 4: Culture of differentiated Caco-2 monolayers with HA35 prevented ethanol-induced disruption of tight junctions.
(A/B/C) Caco-2 monolayers were differentiated for 21 days and then treated or not with 100 μg/ml HA35 for 24 hours, followed by challenge with or without 40 mM ethanol for 3 hours. (A) Cells were then fixed in methanol and immunoreactive ZO-1 (green) and occludin (red) visualized by confocal microscopy. Images acquired at 63X with a 3X digital magnification and are representative of at least two images per slide from three independent experiments. (B) Occludin and ZO-1 expression was assessed by immunoblot using ß-actin as a loading control. Semi-quantification of protein expression was performed using Carestream Imaging Software. (C) FITC-dextran (4Kd) was added to the upper chamber of the transwells and leakage into the lower chamber assessed at 1 and 2h. (D) Differentiated Caco-2 monolayers were treated with increasing concentrations of HA35 for 24 h and then challenged with 500 mM ethanol. TEER was measured immediately before the addition of ethanol and 3 h later. Values are expressed as means ±SEM, (A) n=3, (B) n=4–6 and (C) n=12 (values with different superscripts are significantly different within a time point, p<0.05) and (D) n=4 (*p < 0.05 compared to cells not treated with HA35)