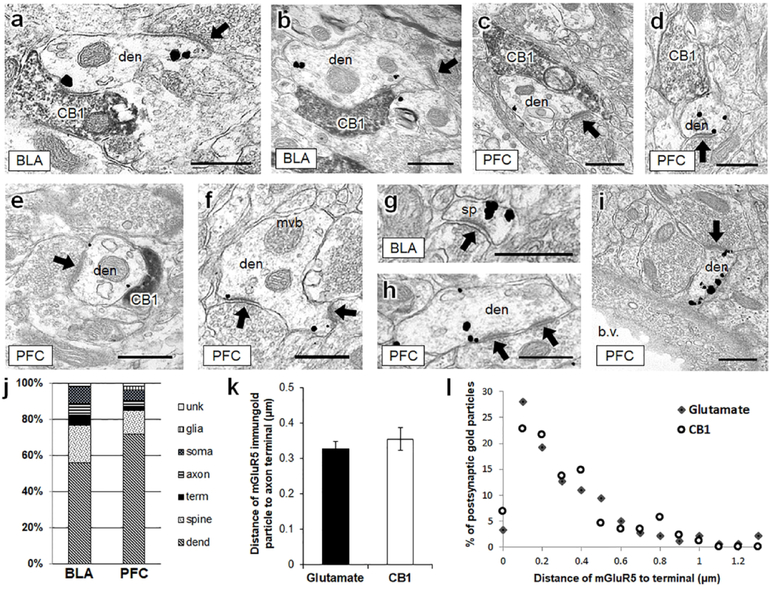
Figure 4: In the BLA and PFC, mGluR5 immunogold is frequently contained within dendrites that are targeted by both CB1-containing axon terminals and glutamatergic axon terminals.
(a, b), In the BLA, dendrites containing punctate mGluR5 immunogold labeling are frequently contacted by CB1-containing axon terminals. These same dendrites also frequently form asymmetric excitatory-type postsynaptic densities with unlabeled terminals (black arrows). (c-e) The same synaptic motif is evident in mGluR5-containing dendrites of the PFC. (f-i) mGluR5 immunogold is also often seen in dendrites and dendritic spines without visible CB1 input. CB1 = CB1-containing axon terminal, den = mGluR5 dendrite, mvb = multi-vesicular body, sp = dendritic spine, b.v. = blood vessel. Scale bars = 500 nm. (j) In 865 mGluR5 labeled profiles counted in the BLA and PFC, mGluR5 immunogold was most frequently contained within dendrites and dendritic spines. (k) The distance of mGluR5 immunogold particles from glutamatergic and CB1-containing axon terminals is not significantly different in the PFC. (l) The distribution of mGluR5 immunogold particle distance from unlabeled glutamatergic terminals and CB1-containing terminals was binned by 0.1 μm increments. The distance between postsynaptic mGluR5 immunogold and CB1-containing or glutamate terminals follows a similar pattern. Unk = unidentifiable (unknown) profile, term = axon terminal, dend = dendrite.