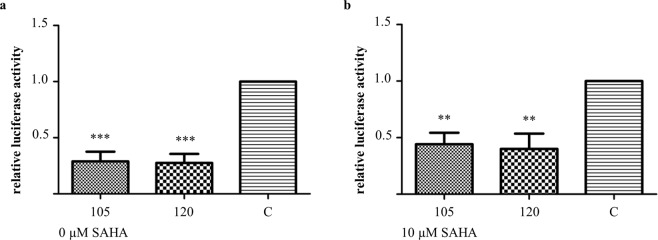
Figure 7.
p53 DBD Nbs have an inhibitory effect on the transcriptional activity of p53. The functionality of p53 as a transcriptional transactivator was evaluated by means of a transactivation assay. HeLa cells were co-transfected with a FLAG-tagged p53 DBD Nb and a pGL13 luciferase reporter. The luciferase activity is representative for the activity of p53 as transcriptional transactivator. A negative control (C) was included whereby HeLa cells were co-transfected with a FLAG-tagged GFP Nb and the pGL13 luciferase reporter. The transfected cells received (or did not receive) an additional treatment with 10 µM SAHA for a duration of 20 h. Luciferase activity was measured 48 h after transfection. Values represent the mean luciferase activity relative to the negative control (±SEM) measured for triplicate samples in 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed via a one-way ANOVA, with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test with a p-value < 0.05. (a) In the absence of SAHA treatment, the p53 DBD Nbs were responsible for a significant reduction of the transactivation activity of p53 compared to the control condition. The relative luciferase activity was reduced by 71% and 72% after transient expression of p53 DBD Nb105 and p53 DBD Nb120, respectively (p < 0.001) (b) Similar observations were made when the transfected HeLa cells received the co-treatment with 10 µM SAHA. In the presence of p53 DBD Nb105, the relative luciferase activity was reduced by 56%. When p53 DBD Nb120 was expressed, the luciferase activity was lowered with 60% (p < 0.01).