Fig. 1.
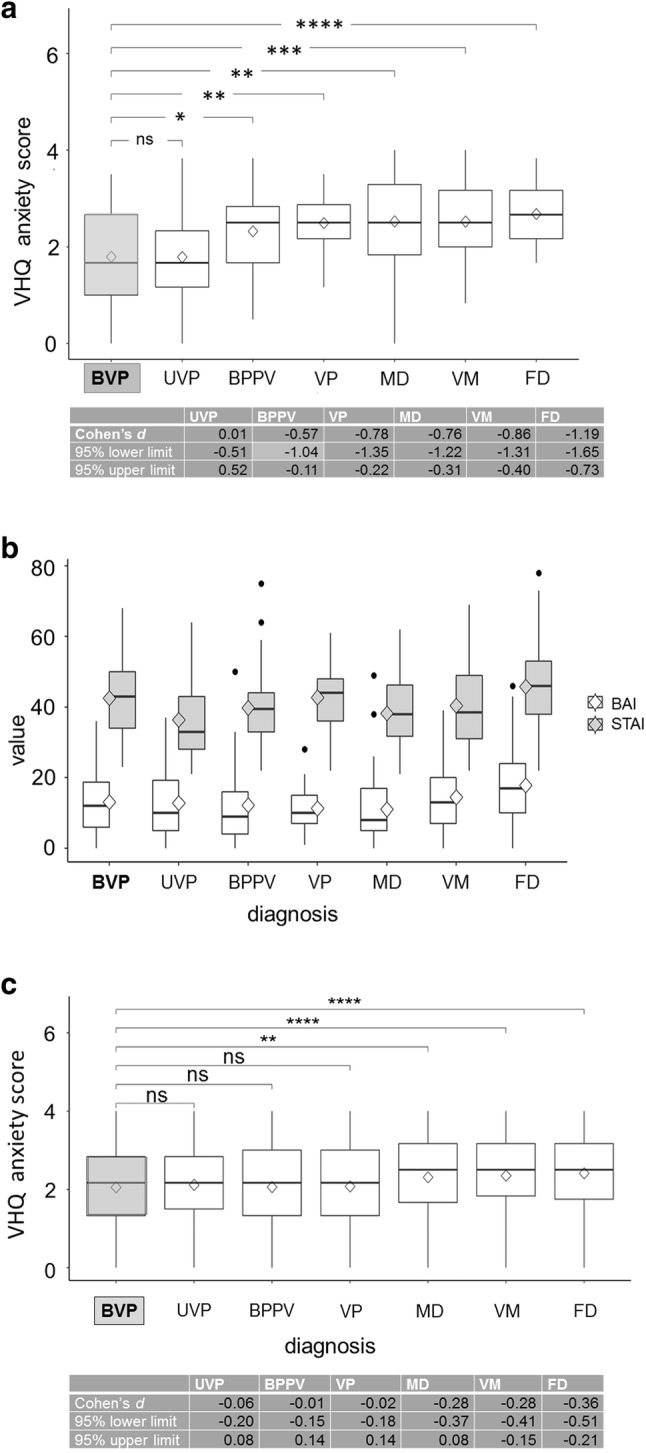
a Vertigo Handicap Questionnaire (VHQ) anxiety score boxplots from different vestibular syndromes of consolidated data sets from patient group 1 (n = 687) for each disease and a t test significance level compared to the reference group of bilateral vestibulopathy (BVP) (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001, ns p > 0.05). Vestibular syndromes were bilateral vestibulopathy (BVP), unilateral vestibulopathy/vestibular neuritis (UVP), benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular paroxysmia (VP), Menière’s disease (MD), vestibular migraine (VM), and functional vertigo/dizziness (FD). Note that the scores were lowest for BVP and UVP and highest for MD, VM, and especially for FD. Median (horizontal solid line), mean (diamond square), boxplot rectangle (lower 25% quantile and higher 75% quantile). A quantification of the effect size magnitude was performed using the thresholds defined in Cohen [20], i.e., Cohen’s d. The magnitude was assessed using the thresholds provided in Cohen [20], i.e., |d| < 0.2 negligible, |d| < 0.5 small, |d| < 0.8 medium, otherwise large. Cohen’s d is given with 95% lower and upper limits for each disease. b For data set 1 (n = 687), in which the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID-I) was performed, BAI (Beck Anxiety Inventory; white) and STAI (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; grey) score value boxplots and outliers (black dots) are given for each disease to show that the low VHQ anxiety scores are not associated with psychiatric comorbidity (anxiety disorders). Cut-off ranges for the BAI have been suggested as follows: 0–7 (no or minimal anxiety), 8–15 (mild anxiety), 16–25 (moderate anxiety), and above 25 (severe anxiety). The STAI cut-off values proposed in the literature for clinically relevant anxiety effect are 39–40 for the original English version. c VHQ anxiety score boxplots from different vestibular syndromes of consolidated data sets from patient groups 1 and 2 (n = 3830) for each disease and a t test significance level compared to the reference group of BVP (**p ≤ 0.01; ****p ≤ 0.0001; ns p > 0.05). A quantification of the effect size magnitude was performed using the thresholds defined in Cohen [20], i.e., Cohen’s d. Cohen’s d is given with 95% lower and upper limits for each disease
