Figure 2.
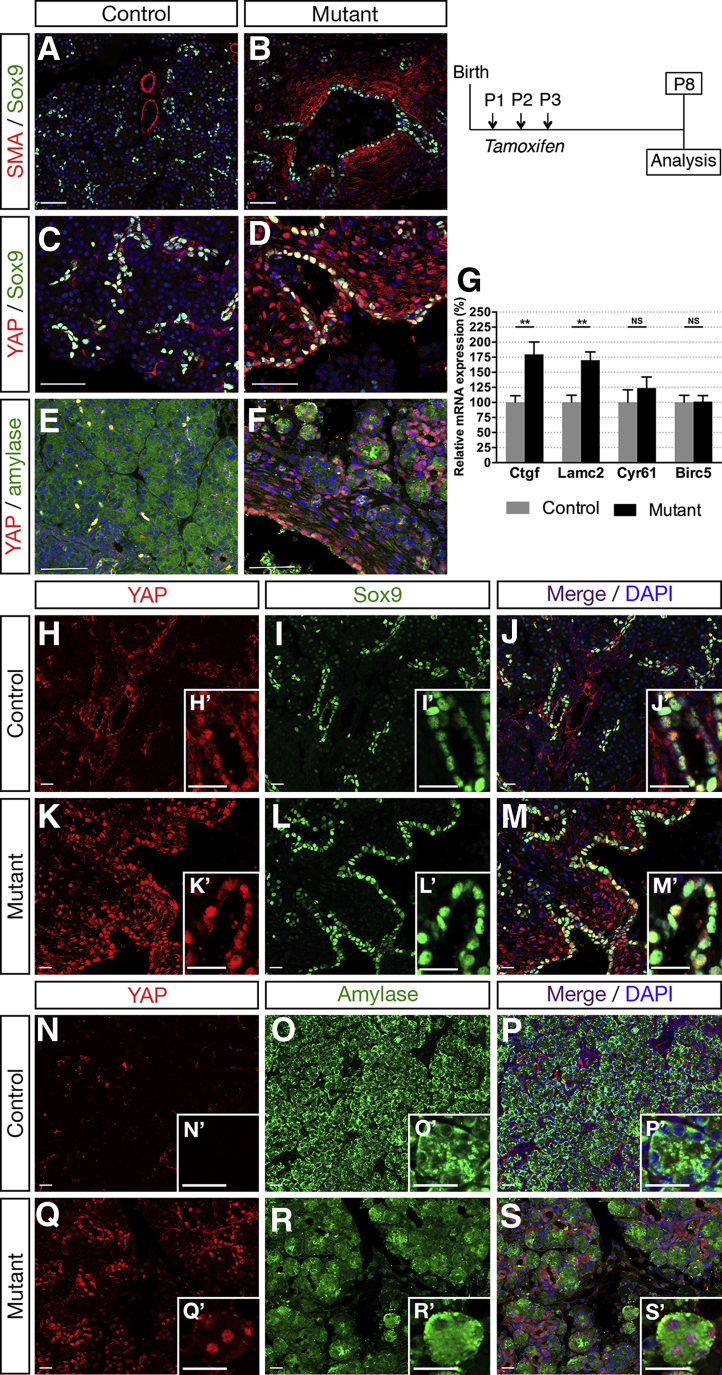
Ductal deletion of Hnf1b leads to up-regulation of the YAP pathway at P8. (A and B) Sox9 (green) and α-SMA (red) immunostaining. α-SMA staining was observed in smooth muscle cells in vessel walls in (A) controls, whereas SMA was activated ectopically in periductal cells in (B) mutants. (C and D) YAP (red) and Sox9 (green) immunostaining. (E and F) YAP (red) and amylase (green) immunostaining. (D and F) Nuclear YAP immunostaining is localized ectopically in periductal and acinar cells in mutants. (G) RT-qPCR analysis of YAP transcriptional targets. (H–M) YAP (red) and Sox9 (green) immunostaining. Merged images show YAP/Sox9 colocalization in ductal cells in (J’) controls and (M’) mutants. (N–S) YAP (red) and amylase (green) immunostaining. No YAP/amylase colocalization is present in (P’) controls, whereas amylase+ cells show YAP+ nuclear staining in (S’) mutants. Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Scale bars: (A–F) 50 μm; (H–S) 20 μm. **P < .01. Control, n = 7; mutant, n = 7 for RT-qPCR and control, n ≥ 3; mutant, n ≥ 3 for immunostainings.