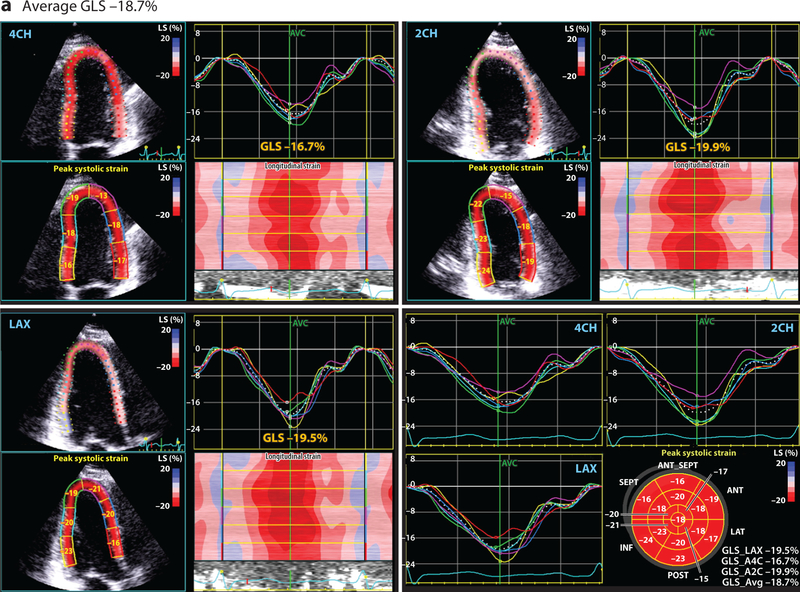
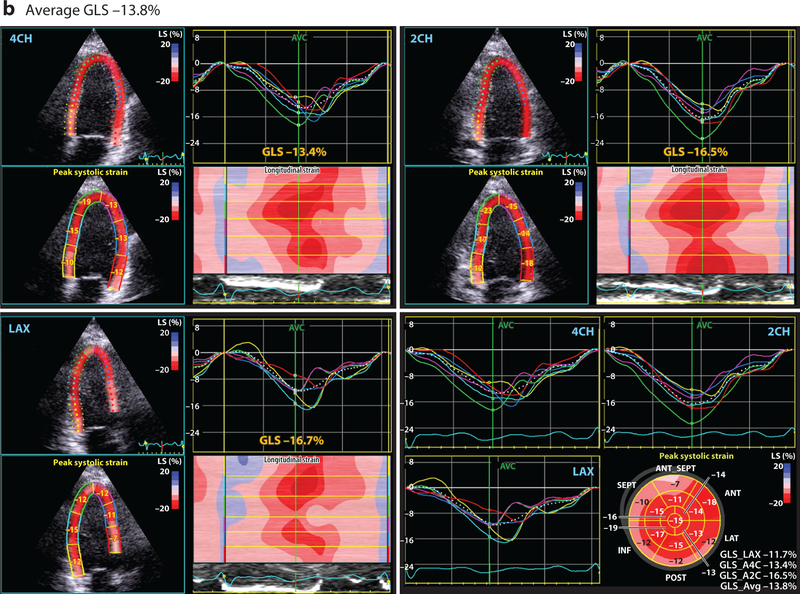
Figure 1.
This four-paneled figure represents the global longitudinal strain (GLS) derived from a breast cancer patient, averaged from the following apical views: LAX (long axis), 2CH (two chamber), and 4CH (four chamber). The lower right panel demonstrates the summary values from each of these views and bullseye plot. Peak systolic GLS is a measure of cardiac deformation that can be readily derived by echocardiography using speckle tracking that provides insight into systolic function. At baseline (a), prior to any cardiotoxic cancer therapy, the average GLS is normal at –18.7%. However, (b) after 240 mg/m2 doxorubicin therapy (and prior to the initiation of trastuzumab), the GLS is reduced at –13.8%, suggestive of subclinical cardiac dysfunction. The GLS was reduced at this timepoint despite a normal estimated left ventricular ejection fraction.