Fig.6.
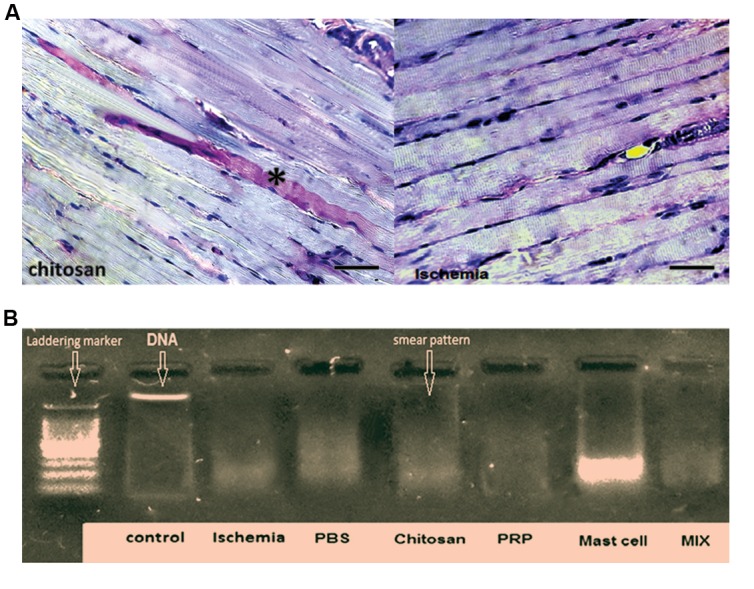
Illustration of PAS staining method and DNA fragmentation analysis of gastrocnemius muscles. A. Representative micrograph showing pink-red periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining to assess muscle glycogen. PAS staining was intense in some muscle fibers (*) but overall was nearly the same for all groups and B. DNA was isolated from rat muscle and prepared for the DNA fragmentation analysis. Ischemia induced DNA smearing considered a marker of necrosis, which was not affected by any of the interventions studied. The left column is a DNA marker indicating DNA “laddering,” associated with apoptosis. All sham and treated groups demonstrate a “smear” pattern, indicating the typical sign of necrosis (100-3000 bp). In this study, we used 5 animals in each group.
