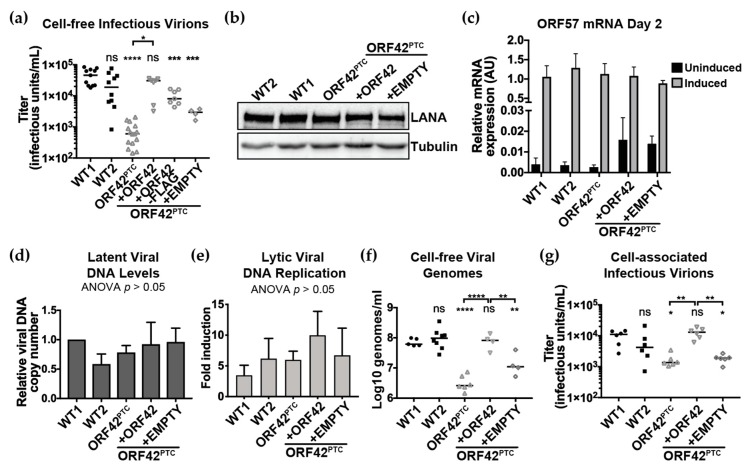
Figure 2.
KSHV ORF42PTC mutations reduce virion formation. The lytic cycle was induced in the indicated infected iSLK.RTA cells by addition of doxycycline (1 μg/mL) to the media. In addition to WT1, WT2 and ORF42PTC, in this and other figures the following labels are used: +ORF42-Flag: KSHV ORF42PTC-infected cells transduced with C-terminally Flag-tagged ORF42; +ORF42: KSHV ORF42PTC-infected cells transduced with untagged ORF42; +EMPTY: KSHV ORF42PTC-infected cells transduced with empty vector. (a) The supernatant from lytically reactivated cells was collected six days after induction and used to infect HEK293T target cells to estimate levels of cell-free infectious virions. Infectious units were calculated from the percentage of GFP-positive target cells measured by flow cytometry. (b) Protein lysates were collected from the indicated latently KSHV-infected iSLK.RTA cells. The latent protein LANA and the cellular protein β-tubulin were detected by Western blotting. (c) Cells were treated with doxycycline (induced) or left untreated (uninduced). mRNA was collected 2 days after induction and RT-qPCR was used to measure the levels of the viral mRNA ORF57 and cellular 18S rRNA. ORF57 levels are reported after normalization to 18S. All differences between induced and uninduced were statistically significant using ANOVA followed by Sidak’s corrected multiple comparison test (p < 0.0001), but there was no significant difference between ORF57 levels in lytic (induced) cells among the strains (p > 0.05, ANOVA followed by Sidak’s corrected multiple comparison test). (d–e) Total DNA was collected prior to induction and four days post-induction. qPCR was used to quantify levels of the viral gene LANA and the cellular gene CCR5. For (d), latent viral copy numbers are plotted relative to WT1 after normalization to CCR5. For (e), the fold increase in DNA levels after induction was calculated after normalization to CCR5 levels. For panels d and e, there is no statistically significant differences between any of the conditions, ANOVA p > 0.05. (f) The supernatant from lytically reactivated cells was collected six days after induction and qPCR was used to quantify viral DNA in supernatant using primers against KSHV LANA. This should estimate viral particle levels, because the samples were treated with DNase to remove unencapsulated DNA prior to DNA isolation. (g) Cell-associated (i.e., intracellular) virions were isolated and used to infect HEK293T target cells. Infection was quantified by determining the percentage of GFP-positive target cells by flow cytometry. For all panels, n ≥ 3. Bar graphs represent mean ± standard deviation. In the other graphs, lines indicate median titers. For panels a, f and g: ns, *,**,**** = p > 0.05, or < 0.05, < 0.01, and < 0.0001 respectively, ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison test. The p values are either for comparisons to WT1 (where no bracket is present) or for the comparison indicated by the bracket. The WT2 vs. ORF42PTC comparison for panels a and f is also significantly different, p < 0.01, ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison test.