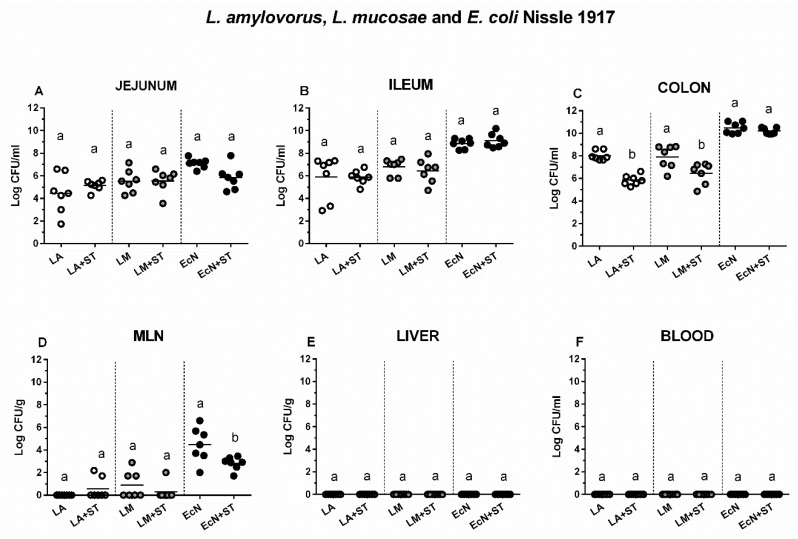
Figure 2.
Colonization and translocation of L. amylovorus, L. mucosae, and E. coli Nissle 1917 in the gnotobiotic piglets. L. amylovorus (LA), L. mucosae (LM), and E. coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) colony forming units (CFU) were counted in the jejunum (A), ileum (B), colon (C), mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN; (D)) the liver (E), and blood (F) in monocolonized piglets (LA, LM, and EcN) and monocolonized piglets infected with S. Typhimurium (LA+ST, LM+ST, and EcN+ST). Interferences between LA, LM, EcN, and ST as LA vs. LA+ST, LM vs. LM+ST, and EcN vs. EcN+ST, respectively were evaluated by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test. Statistical differences were marked by a letter system at P ˂ 0.05. The same letter means no statistical significance. Log CFU are depicted as individual spots with mean as a horizontal line and n = 7 for all groups.