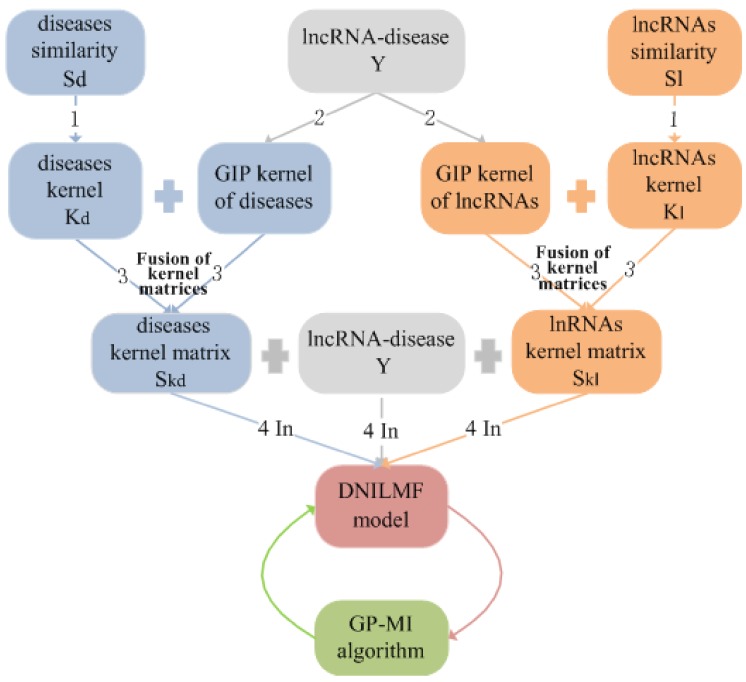
Figure 1.
The flowchart of dual-network integrated logistic matrix factorization-lncRNA–disease association (DNILMF-LDA). Step 1: converting the calculated lncRNAs’ similarity matrix and the diseases’ similarity matrix to the corresponding kernel matrix; Step 2: calculating the Gaussian interaction profile kernel matrix of lncRNAs and diseases, respectively; Step 3: fusing two kernel matrices corresponding to the lncRNAs and the diseases respectively into one kernel matrix; Step 4: constructing the DNILMF model with the lncRNA–disease associations matrix, lncRNAs, and diseases kernel matrices as the input data. In order to ensure the optimal performance of the algorithm, the Gaussian process mutual information (GP-MI) algorithm is used to select parameters. GIP, Gaussian interaction profile.