Figure 3.
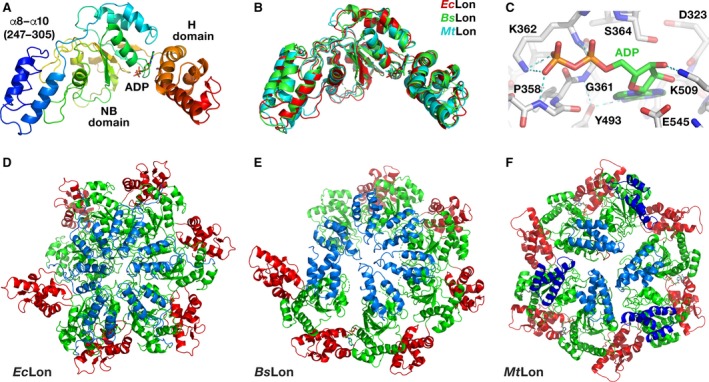
Structures of LonA proteases. (A) Crystal structure of a truncated fragment of EcLon (residues 235–584 in rainbow coloring). Individual domains are marked. The bound ADP molecule is shown in sticks. (B) Superposition of the crystal structures of three similar fragments of EcLon (red), BsLon (green) and MtLon (cyan). (C) Interactions of ADP molecule in the binding pocket of EcLon. (D) Cartoon representation of an open ring hexamer in the structure of EcLon (235–584), with helical arrangement of the monomers around the crystallographic 61 axis passing through the central pore. N‐terminal helices are blue, NB domains are green, and H domains are red. (E) Crystal structure of the open hexamer of BsLon (240–774; PDB ID 3M6A, P domain not shown for clarity). Colors are as in panel D. (F) Crystal structure of the closed hexamer of the fragment (242–793) of MtLon (PDB ID 4YPL, P domain not shown for clarity). Two sets of N‐terminal three‐helix bundles located either at the center or at the periphery of a hexamer are shown in light and dark blue, respectively.
