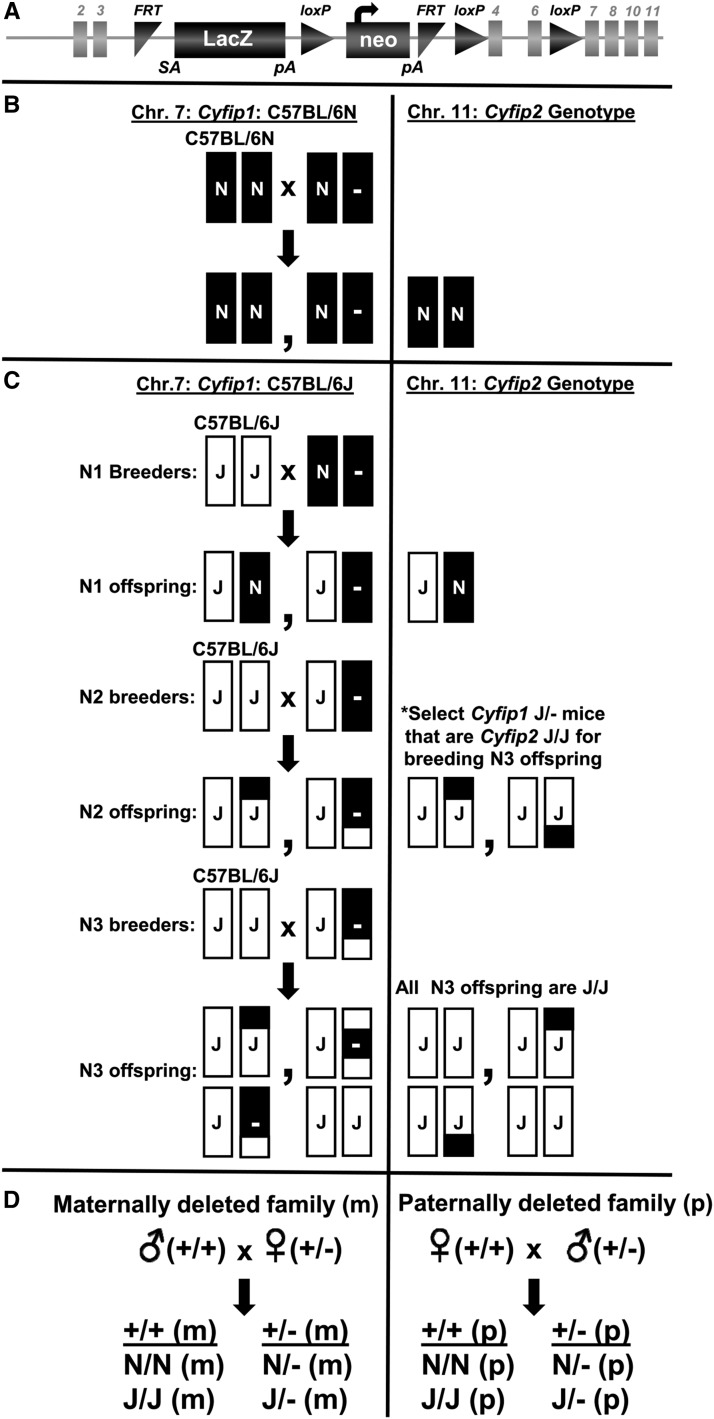
Figure 1.
Generation of the Cyfip1 knockout allele and breeding scheme for Cyfip1 haploinsufficient mice on the Cyfip1,2N/N and Cyfip1,2J/J genetic backgrounds. (A): A schematic of the knockout first allele for KOMP generation of Cyfip1N/- mice was obtained from the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC) website (http://www.mousephenotype.org/data/alleles/MGI:1338801/tm2a(EUCOMM)Wtsi). Mice containing floxed alleles flanking exons 4 through 6 were generated from embryonic stem cells on a C57BL/6N background by the International Knockout Mouse Consortium and were crossed to global Cre-expressing mice, yielding offspring heterozygous for constitutive deletions in exons 4 through 6. Mice heterozygous for the null deletion on a C57BL/6N background were re-derived using sperm obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. (B): Left panel: In the first study, we re-derived Cyfip1N/- and propagated mice on an isogenic C57BL/6N background. Right panel: All mice were homozygous for the N allele (N/N) at Cyfip2 which contains a missense mutation that we previously showed was associated with a marked enhancement of binge eating (BE), accounting for one-third of the genetic variance in parental strain BE (Kirkpatrick et al. 2017). We maintained this colony on an isogenic C57BL/6N background by breeding Cyfip1N/- mice with C57BL/6NJ mice (black bars; N/N) ordered from The Jackson laboratory. (C): In the second study, we generated another colony on a mixed background. The primary goal was to monitor and replace the BE-associated N/N Cyfip2 alleles with C57BL/6J (J/J) alleles via backcrossing Cyfip1N/- mice to C57BL/6J (white bars; J/J) for three and four generations and assess the effect of Cyfip1 deletion on BE on a mixed N3 and N4 background containing a fixed, BE-resistant, homozygous J/J genotype at Cyfip2 (Kirkpatrick et al. 2017). Mixed-color bars illustrate hypothetical recombination events that accumulate through repeated backcrossing to C57BL/6J (white). (D): Schematic of the bidirectional, parent-of-origin crosses for generating wild-type (+/+) and heterozygous (+/−) offspring from either the paternally (p) deleted Cyfip1 families or the maternally (m) deleted Cyfip1 families. There are eight possible annotations, including four on the Cyfip1,2N/N background and four on the Cyfip1,2J/J background. N/N (m): Wild-type offspring from a maternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 N/N background; N/- (m): Heterozygous offspring from a maternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 N/N background; N/N (p): Wild-type offspring from a paternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 N/N background; N/- (p): Heterozygous offspring from paternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 N/N background; J/J (m): Wild-type offspring from a maternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 J/J background; J/- (m): Heterozygous offspring from a maternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 J/J background; J/J (p): Wild-type offspring from paternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 J/J background; J/- (p): Heterozygous offspring from a paternally deleted family on a Cyfip1,2 J/J background.