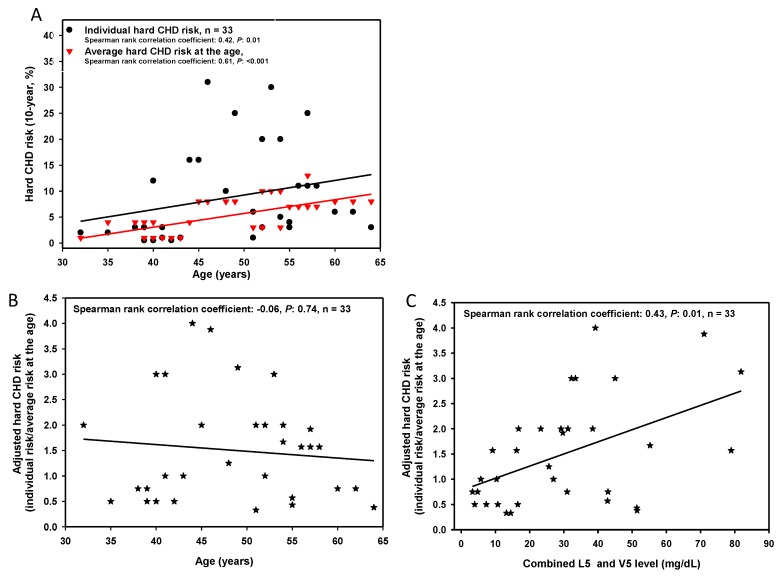
Figure 1.
The relationship between combined L5 and V5 levels and coronary heart disease (CHD) risk according to the Framingham risk score. (A) Correlation between age and 10-year hard CHD (i.e., myocardial infarction, coronary death, or stroke) risk according to the Framingham risk score. (B) Correlation between age and adjusted hard CHD risk (i.e., hard CHD risk/average hard CHD risk at the age). The average hard CHD risk at the age is derived from the Framingham Heart Study [25] of a predominantly Caucasian population in Massachusetts, USA. (C) Correlation between the combined amount of L5 and V5 and adjusted hard CHD risk.