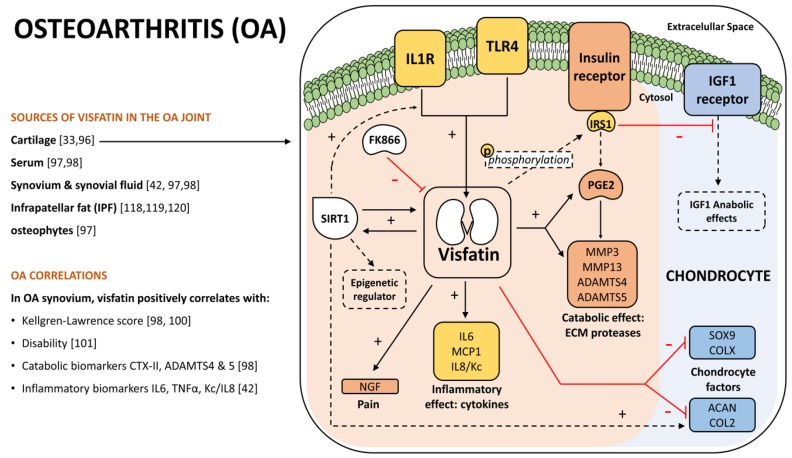
Figure 3.
Visfatin Role in Osteoarthritis (OA). Visfatin is involved in OA. Visfatin positively correlates with several disease markers in the OA synovium. In the OA chondrocyte, visfatin expression is promoted by interleukin-1 receptor (IL1R) and innate immune toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and blocked by the specific inhibitor FK866. Visfatin promotes inflammatory effects, inducing the expression of cytokines, metalloproteinases, and synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Visfatin also works as an epigenetic regulator through its interaction with Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). Furthermore, visfatin inhibits chondrocyte anabolism. Interleukin 6 (IL6); Interleukin 8 (IL8), also known as chemokine (Kc); monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1); insulin receptor (IR); insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1); insulin-like growth factor (IGF1); extracellular matrix (ECM); matrix metalloproteinases 3 (MMP3) and 13 (MMP13); disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs 4 (ADAMTS4) and 5 (ADAMTS5); SRY-box 9 (SOX9); collagen type 10 (COLX) and type 2 (COL2); aggrecan (ACAN); nerve growth factor (NGF).