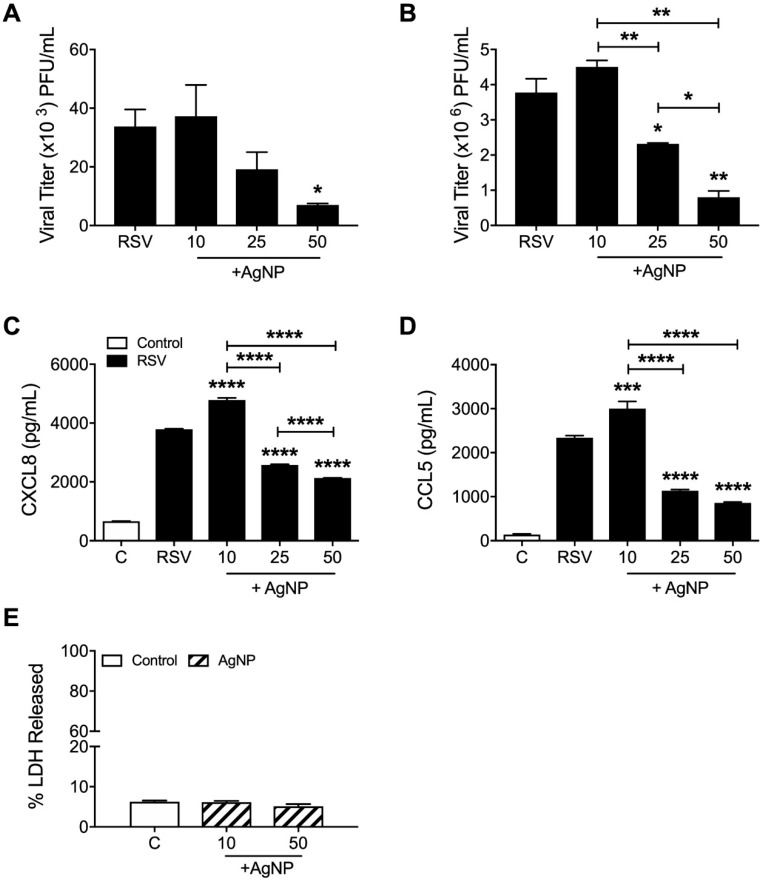
Figure 1.
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) decreased respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) replication in epithelial cell lines. (A) A549 cells were infected with RSV or AgNP-RSV (0, 10, 25, or 50 μg/mL) at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 and (B) HEp-2 cells were infected with RSV or AgNP-RSV at an MOI of 0.01. Supernatants of infected cells were collected as described in the methods. Viral replication was determined by plaque assay and (C) CXCL8 and (D) CCL5 levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (E) The toxicity of AgNPs (0, 10, and 50 μg/mL) on A549 cells was determined using LDH as an index of cellular damage. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and is representative of three independent experiments. Significant results as compared to the RSV control are marked with asterisks, and additional comparisons between groups are indicated with brackets (* for p ≤ 0.05, ** for p ≤ 0.01, *** for p ≤ 0.001, **** for p ≤ 0.0001).