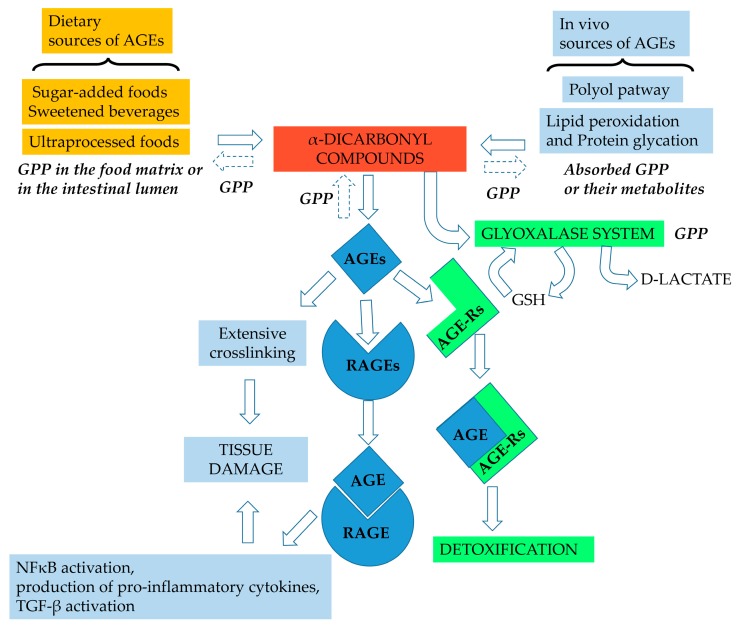
Figure 2.
Potential sites of action of grape pomace phenolics (GPP) in the glycation pathway. In the food matrix during processing and in the intestinal lumen, GPP can inhibit α-dicarbonyl compounds and AGE formation by acting as metal chelators, antioxidants and carbonyl trapping agents. Absorbed GPP or their metabolites can exert the same activities in vivo; moreover, GPP can assist the detoxifying process in vivo by acting as a glyoxalase inducer. GSH, reduced glutathione; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, TGF-β transforming growth factor β.