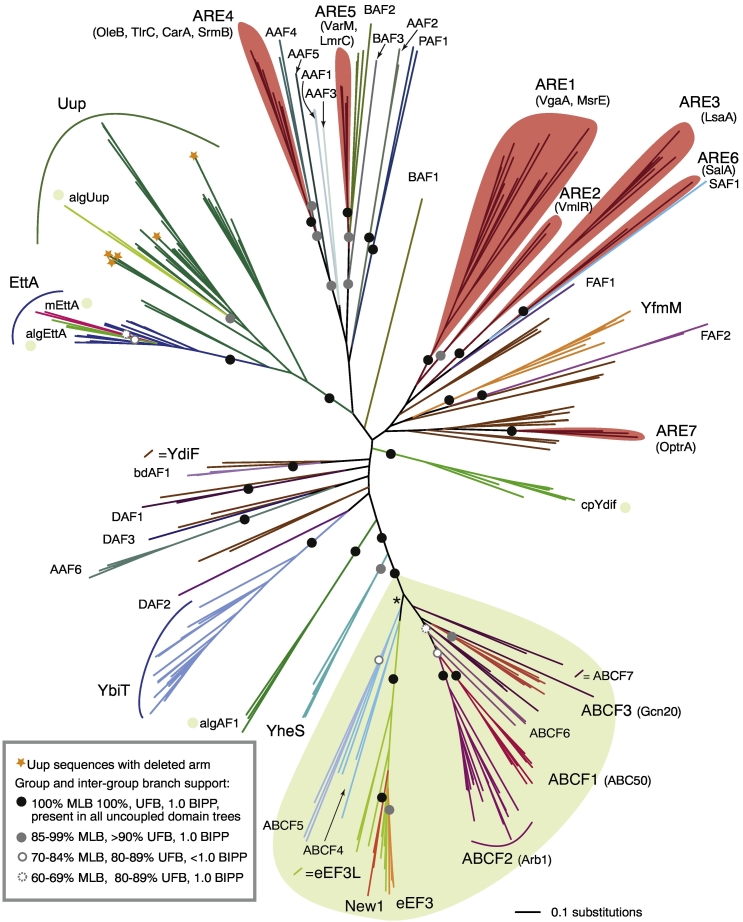
Fig. 1.
The family tree of ABCFs has a bipartite structure corresponding to eukaryotic-like and bacterial (and organellar)-like sequences. The tree is a RaxML maximum likelihood phylogeny of representatives across the ABCF family with branch support values from 100 bootstrap replicates with RaxML (MLB), 1000 UFB replicates with IQ-TREE and BIPP. The inset box shows the legend for subfamily and intersubfamily support; support values within subfamilies and that are less that 60% MLB are not shown. Species were chosen that sample broadly across the tree of ABCF-encoding life, sampling at least one representative from each subfamily. Green shading shows the eukaryotic type ABCFs; other subgroups are bacterial unless marked with a green shaded circle to indicate eukaryotic groups with potentially endosymbiotic origin. CpYdif contains both cyanobacterial and predicted chloroplast sequences. The full tree with taxon names and sequence IDs is shown in Fig. S1. Branch lengths are proportional to amino acid substitutions as per the scale bar in the lower right. The asterisked branch is not supported by this data set; however, it is supported at 85% MLB in phylogenetic analysis of the eukaryotic subgroup and its viral relatives, rooted with YheS (Fig. S3).