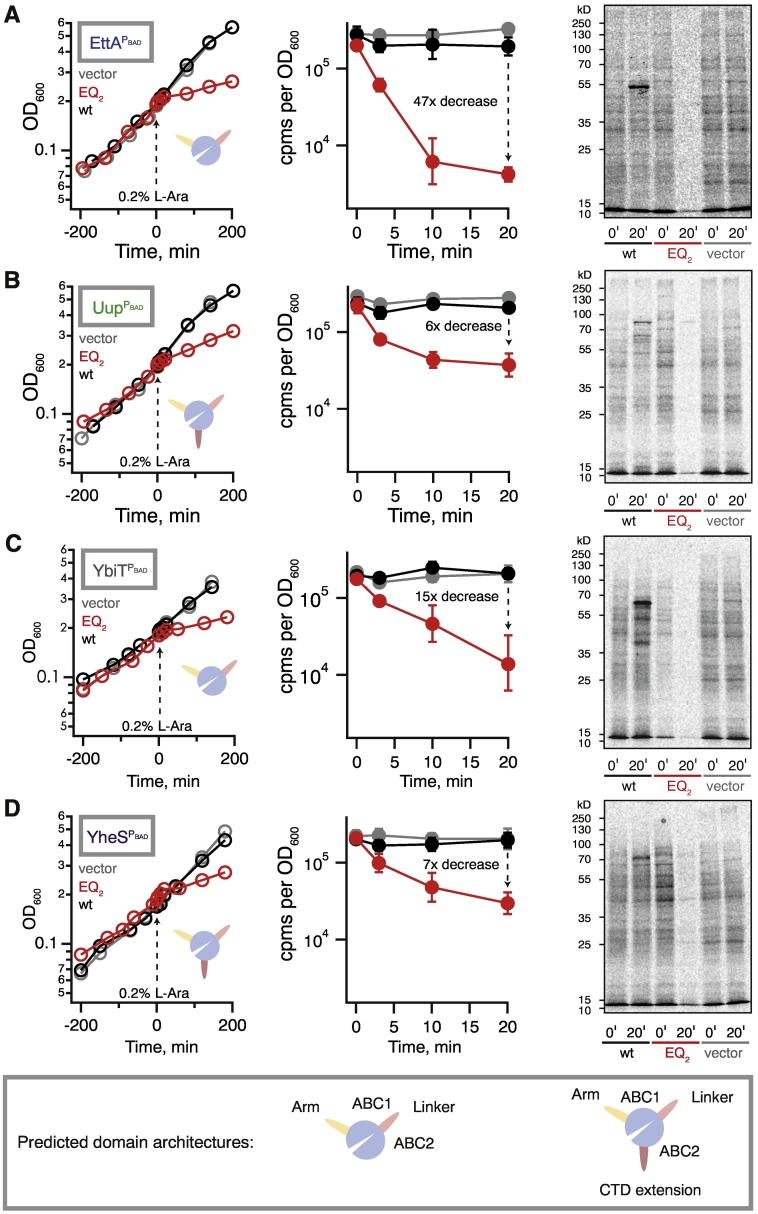
Fig. 6.
Expression of E. coli ABCF-EQ2 mutants inhibits growth and protein synthesis.
Growth of wild-type E. coli BW2513 transformed with pBAD18 vector (gray trace) as well as E. coli BW2513 expressing either wild-type (black trace) or EQ2 mutants (red trace) of EttA (A), Uup (B), YbiT (C), and YheS (D) under the control of arabinose-inducible promoter PBAD. Radiographs show the effect of wild-type and EQ2 ABCF expression on protein synthesis, as probed by pulse labeling with l-[35S]-methionine. Expression was induced by the addition of l-arabinose to a final concentration of 0.2% at time point 0, and efficiency of incorporation was quantified by scintillation counting and visualized by autoradiography at 0- and 20-min time points. Scintillation counting data are presented as geometric means ± standard deviation (n = 3). All experiments were performed at 37 °C in Neidhardt MOPS medium [80] supplemented with 0.4% glycerol as a carbon source. The inset cartoons are a representation of ABCF domains and sub-domains, as per the legend in the lower box.