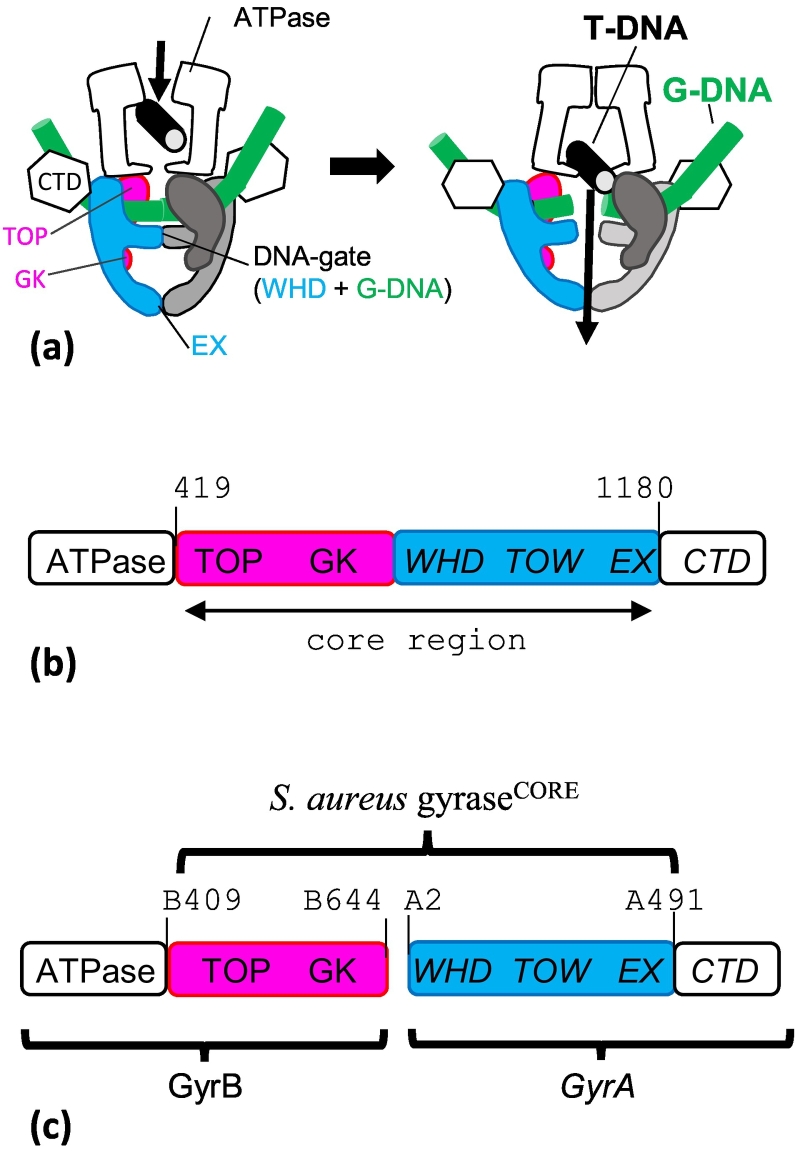
Fig. 1.
Schematic of type IIA topoisomerases. (A) Simplified schematic of the action of type IIA topoisomerases, such as yeast topoisomerase II (topo II), DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. A segment of DNA (T-DNA) is transported by capture through the ATPase domains interface and passes through a transient double-strand break established in the G-DNA (forming a DNA “gate” interface with the WHD domain). The DNA then exits the enzyme through the exit gate (EX). (B) Eukaryotic topo IIs are homodimers, and many key structures have been determined with a “core’ region (419–1180) encompassing the TOPRIM domain (TOP), the Greek key fold, the winged-helix domain (WHD), the Tower (TOW) and the exit gate (EX). (C) Fusing the C-terminal region of S. aureus GyrB (residue 409 to 644) to the N-terminal region of GyrA (residue 2 to 491) gives an “equivalent” construct. The Greek key can be deleted from this core construct in S. aureus gyrase.