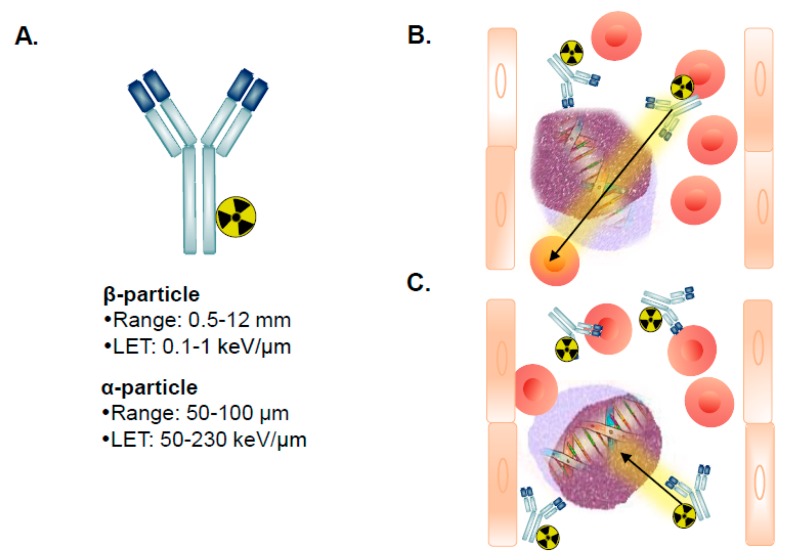
Figure 2.
Radioimmunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Illustration of (A) a mAb radiolabeled with either a (B) β-particle or (C) α-particle-emitting radionuclide and the track of the particles perfusing the bone marrow to target AML cells. Note that the path length of β-particles is greater than for α-particles leading to β-particle-based RIT used primarily in preparative regimens to myeloablate the bone marrow prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation.