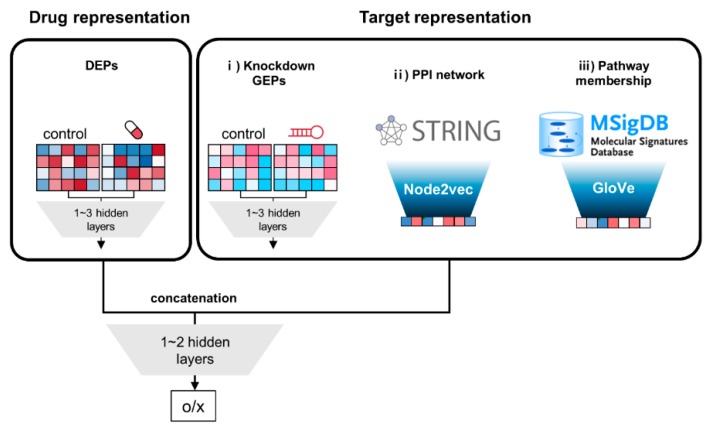
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of deep neural network (DNN) models for comparison of three different target features. First, the model takes two types of input features, i.e., drug and target features, as separate blocks. Drug features are a concatenated vector with 978 + 978 = 1956 elements from both control and treated drug-induced expression profiles (DEPs) from the Library of Integrated Network-based Cellular Signatures (LINCS) L1000 dataset. Target features are obtained from three sources: (i) knockdown gene expression profiles (GEPs); (ii) protein–protein interaction (PPI) network; and (iii) pathway membership. Target features of GEPs are set to the same structure of 1956-element vectors as drug features. Both features for DEPs and GEPs are connected to 1~3 hidden layers. The target features for the PPI network and pathway membership were extracted by node2vec and Glove method, respectively without hidden layer. The output values of drug and target blocks are concatenated, and subsequently feed to additional 1~2 hidden layers, leading to the final output.