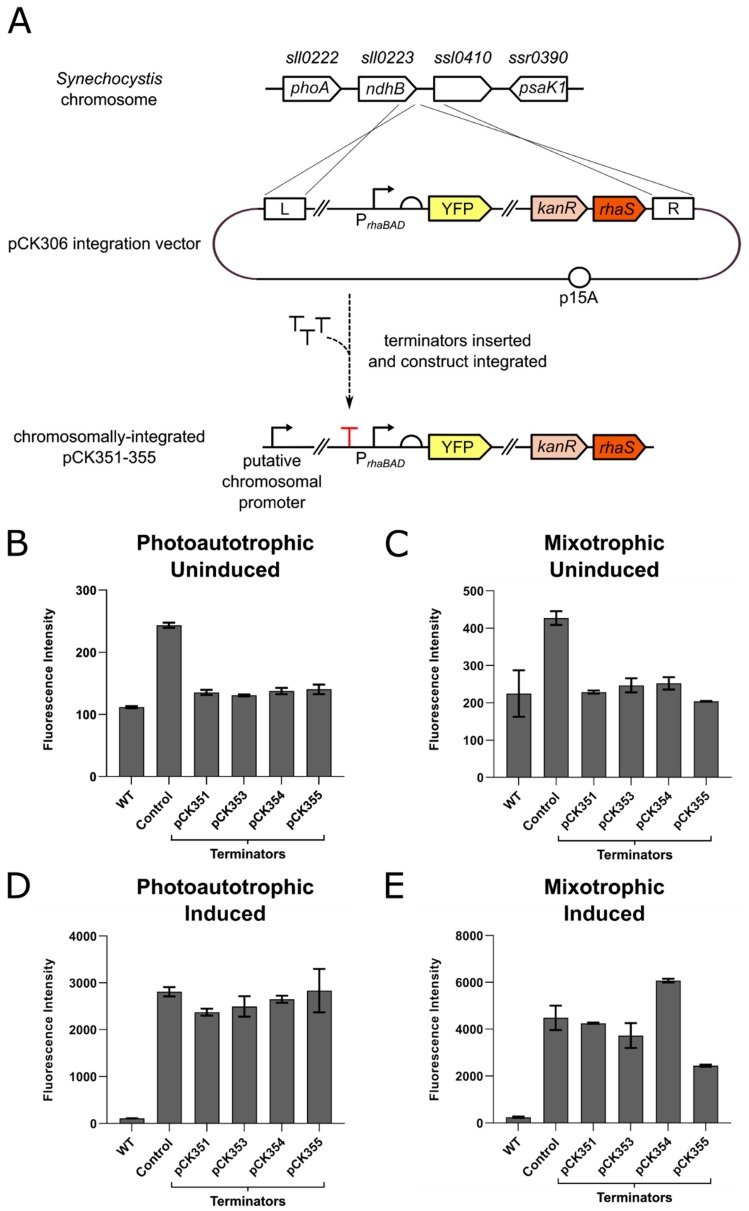
Figure 2.
The effect of terminators inserted upstream of a rhamnose-inducible YFP expression construct inserted in the Synechocystis chromosome after 96 h. (A) Detail showing the insertion of terminators into integration plasmid pCK306 upstream of the rhaBAD promoter. The resulting constructs pCK351, pCK353, pCK354 and pCK355 were integrated into the Synechocystis genome adjacent to the ndhB gene. (B) To test for transcriptional insulation from chromosomal promoters after integration, Synechocystis transformants containing the integrated terminator constructs were cultured in BG11 media supplemented with kanamycin and no L-rhamnose, in photoautotrophic conditions and constant light. Wild-type Synechocystis cells (WT) lacking YFP entirely and cells containing pCK306 (no terminator inserted upstream of rhaBAD promoter) were used as controls. The fluorescence intensity (arbitrary units) of 10,000 cells from each culture was measured by flow cytometry at 96 h. (C) Equivalent experiment to (B) but strains cultured in BG11 supplemented with 5 mM D-glucose (mixotrophic growth). (D) The same strains of Synechocystis were cultured in BG11 media supplemented kanamycin and L-rhamnose to a final concentration of 0.6 mg/mL in photoautotrophic conditions and constant light. The fluorescence intensity (arbitrary units) of 10,000 cells was measured after 96 h using flow cytometry. (E) Equivalent experiment to (D) but strains cultured in BG11 supplemented with 5 mM D-glucose (mixotrophic growth). Error bars shown represent the standard deviation of the mean of three independent biological replicates. Key for SBOL glyphs used in figure: right-angled arrow represents a promoter; T represents a terminator; semi-circle represents a ribosome-binding site (RBS); coloured blocks represent coding sequences or genes.