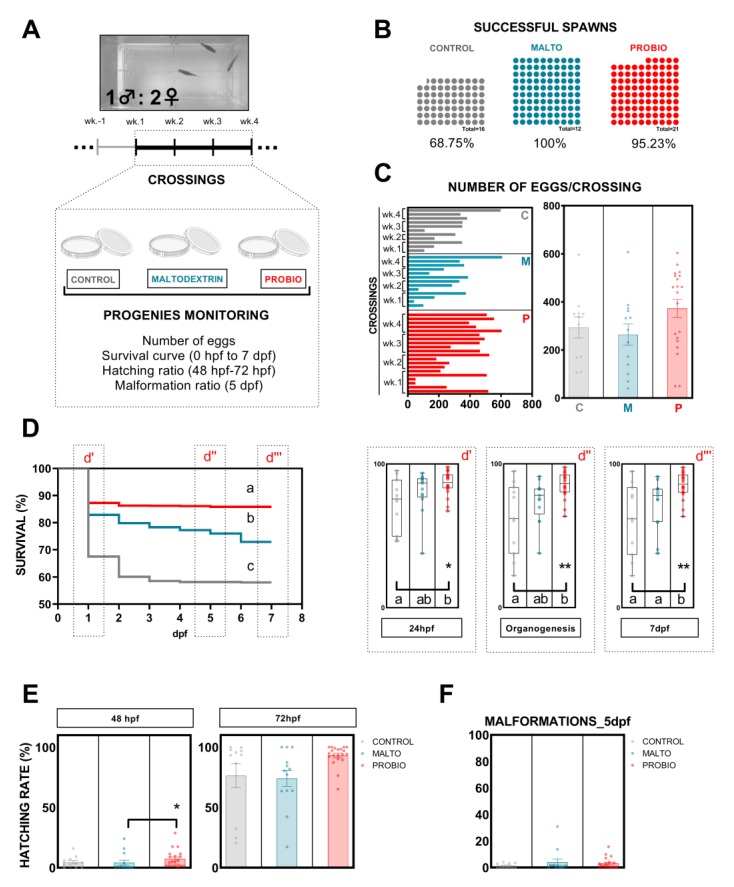
Figure 3.
Probiotic ingestion positively affects zebrafish reproduction in terms of egg production and progeny quality. (A) Diagram summarizing design and all parameters analyzed involving each progeny. (B) The effect of experimental diets on the percentage of successful spawns, (C) total number of eggs spawned per crossing, (D) F1 survival (Kaplan–Meier curves (0–7dpf) and Box graphs (whiskers show min. to max.) at different key temporal points), (E) hatching rate at 48 hpf and 72 hpf, and (F) malformation rate. Data are presented as means ± s.e.m. “CONTROL/C”, “MALTO/M”, and “PROBIO/P” refer to the experimental groups: control diet-fed, maltodextrin-fed, and probiotics-fed, respectively. Asterisks show statistically significant differences: * (p < 0.0500), ** (p < 0.0100), and letters (a, b, c) show statistically significant differences among groups.