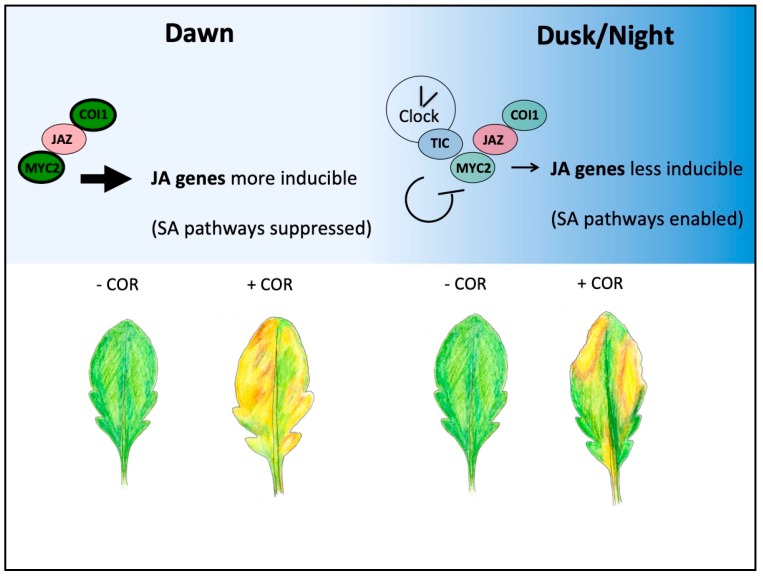
Figure 2.
Gating of JA responses through gene expression control and by TIC. COI1-JAZ-MYC signaling complex positive components (green) and negative components (red) are shown in the morning (left) or evening (right); more intense coloring and darker border indicate higher protein abundance. Throughout the night and at dawn, the clock protein TIC reduces MYC2 protein abundance likely through direct interaction, and it therefore restricts MYC2-dependent actions (right side) [76]. Positive factors of the COI1-JAZ-MYC2 complex (COI1, MYC2) are more abundant at dawn and during the daytime due to transcriptional or post-translational control, and this is one mechanism that gates JA responsiveness to this time of the day. JA early genes (i.e., JAZ5) are most inducible by JA treatment at dawn [76]. The JA mimic coronatine (COR) produced by Pseudomonas syringae (Pst DC3000) hyper-activates the JA pathway and suppresses SA-dependent and independent host defenses against biotrophic pathogens [77,78]. Treatment of plants at dawn with Pst DC3000 results in leaves that support more pathogen proliferation compared to treatment at dusk, although clock-timing of stomata closure that is independent of JA signaling could play an important role too (bottom) [76,79].