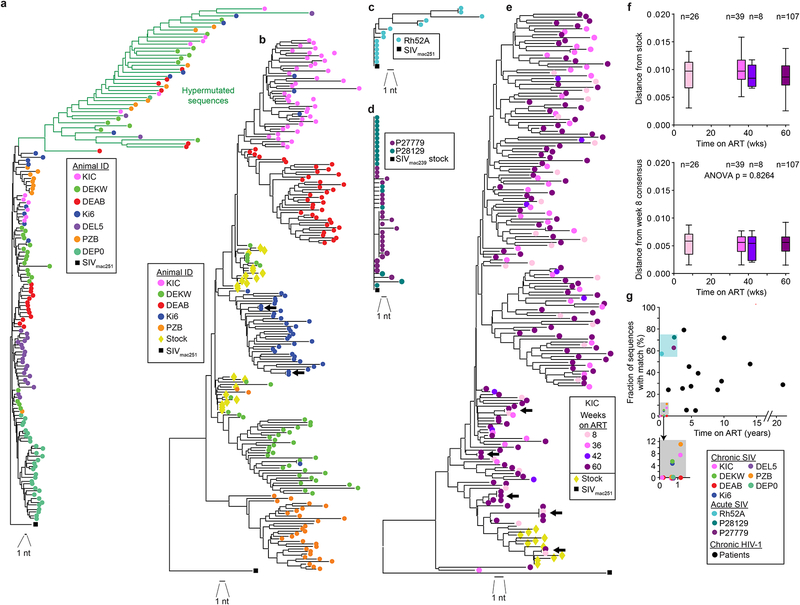
Fig. 4. Identical sequences in SIVmac infection.
(a) Phylogenetic tree of SIV env sequences obtained by near full-genome sequencing from 7 treated animals infected with SIVmac251 and sampled 36 weeks after ART initiation and the SIVmac251 reference sequence (black square). Sequence analysis includes 2044 nt. Hypermutated sequences from each animal clustered together due to commonly mutated positions, (b) Composite phylogenetic tree of env sequences obtained by full-genome sequencing and env SGA along with SIVmac251 stock sequences (yellow diamonds) and the SIVmac251 reference sequence (black square). Hypermutated sequences were omitted. Two pairs of identical sequences potentially representing expanded cellular clones were identified (arrows). Three identical sequences from animal DEKW are intermingled with the stock sequences and may represent infection of multiple cells with the same variant present in the stock, (c) Tree of env sequences from full-genome sequencing on CD4+T cells from a rhesus macaque treated with ART 2 weeks after infection with SIVmac251 and sampled after 19 weeks of treatment. (d) Tree of env sequences from SGA on CD4+ T cells from 2 rhesus macaques treated with ART 6 weeks after infection with SIVmac239 and sampled after 120 weeks of treatment, (e) Representative phylogenetic tree of env sequences obtained by SGA from animal KIC at multiple time points. Arrows indicated identical sequences, (f) Root-to-tip distances for the phylogenetic trees shown in (e), calculated using the stock consensus sequence (top) or the week 8 consensus (bottom) at the root. Data for animal KIC are shown here. Similar plots for animals DEAB, PZB, and DEKW are shown in Fig. S3e–g. (g) Relationship between fraction of clonal sequences and time on ART. Data are from studies using env SGA to analyze viral genomes in SIV-infected macaques (colored symbols) or HIV-1-infected patients on ART for the indicated times. HIV-1 data are from published studies (Bailey et al., 2006; Bar et al., 2016; Bruner et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018).