Figure 3.
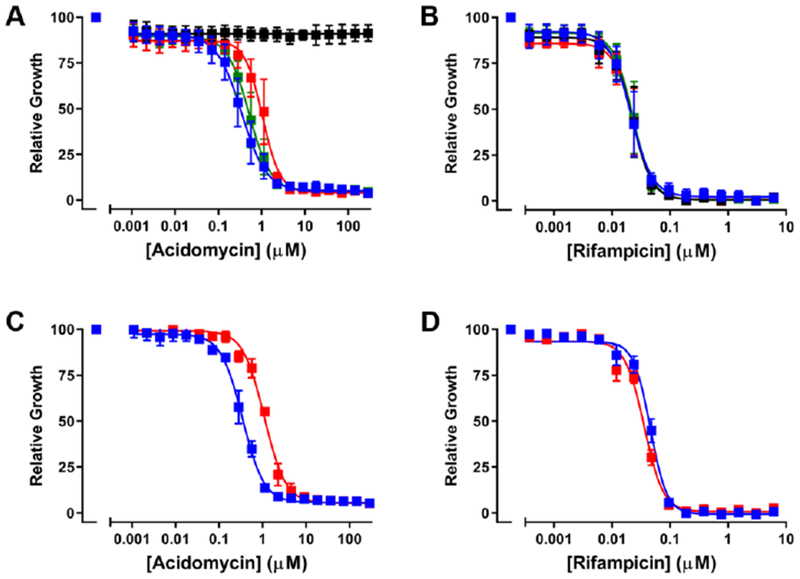
Impact of extrabacterial biotin and overexpression of BioB on susceptibility of M. tuberculosis H37Rv to (±)-acidomycin. Panels A and B show MIC curves for (±)-acidomycin (A) and rifampicin (B) in GAST medium supplemented with 1 μM biotin pathway intermediates (black, biotin; red, DTB; green, KAPA) or DMSO only (blue). Panels C and D show MIC curves for M. tuberculosis H37Rv (blue squares) and the BioB merodiploid strain (red squares) against (±)-acidomycin (C) and rifampicin (D) grown in GAST medium. Normalized growth was calculated at OD580 at the indicated concentration divided by the OD580 with drug (DMSO). Data are averages (± SD) of triplicate cultures and are representative of two independent experiments.
