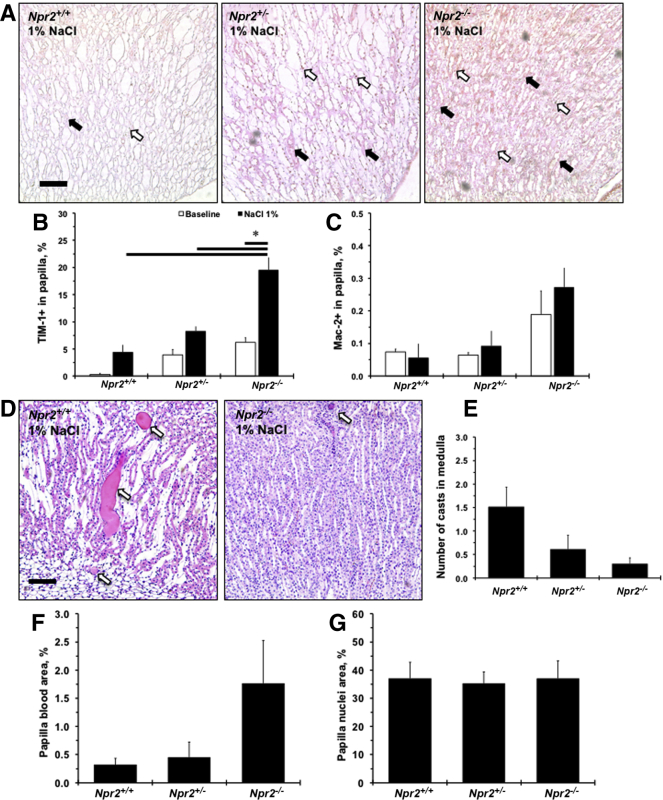
Figure 3.
Histologic evaluation of renal papillary injury across Npr2 genotypes in response to salt. A: Representative images of double-stained [macrophage surface glycoproteins binding to galectin-3 (Mac-2) and T-cell Ig and mucin domain 1 (TIM-1)] kidney papilla across Npr2 genotypes after 1% NaCl intake in drinking water for 2 weeks. White arrows show Mac-2+ cells (brown). Black arrows show TIM-1+ staining (pink). Counterstain is green. B and C: Quantitative analysis of the TIM-1 (B) and Mac-2 (C) expression in the renal papilla in Npr2 mice. D: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin–stained renal medulla of Npr2 wild-type (Npr2+/+) and Npr2 knockout (Npr2−/−) mice after 1% NaCl intake in drinking water for 2 weeks. White arrows point to protein casts. E: Quantitative analysis of protein casts in the renal medulla in Npr2 mice. No protein casts were detected at baseline. F: Quantification of blood in renal papilla in Npr2 mice. G: Quantification of nuclei area in renal papilla in Npr2 mice. White bars are baseline values. Black bars are values after 2 weeks of 1% NaCl intake in drinking water. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 per group (B and C); n = 3 to 5 per group (E–G). ∗P < 0.05 versus Npr2−/− (1% NaCl). Scale bars = 100 μm (A and D). Npr2+/−, Npr2 heterozygous.