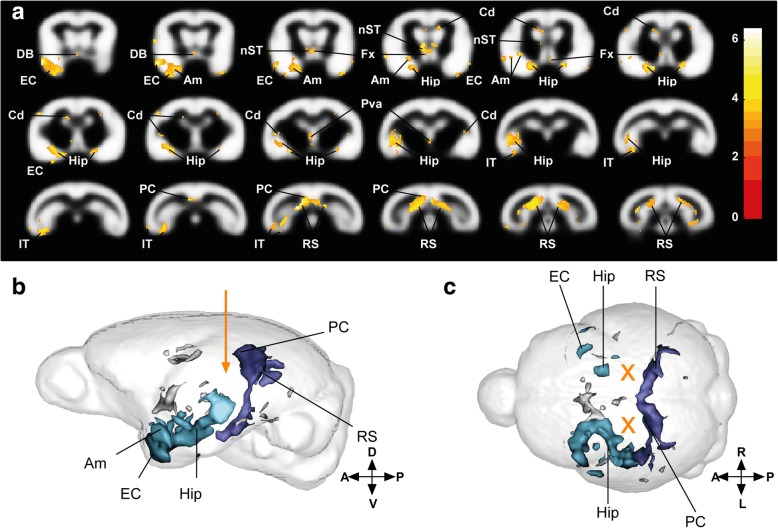
Fig. 3.
Cerebral atrophy in Alzheimer-inoculated compared to control-inoculated mouse lemurs. a Statistical parametric maps depicting regions in which cerebral tissue volume decreased in the Alzheimer-inoculated group compared to the control group. The color-coded blobs show statistical differences between Alzheimer-inoculated animals and control-inoculated mouse lemurs. Images follow the radiological convention (i.e. left hemisphere is on the left). Slices are spaced 0.5 mm apart along the rostro-caudal axis (voxel-based morphometric parameters: FDR-corrected p < 0.05; extent threshold k = 10; map represents t values). Lateral b and (c) dorsal 3D representations of atrophied areas. Orientation of the brain is explained by the crossing arrows, and letters. A: anterior; P: posterior; D: dorsal; V: ventral; L: left; R: right; EC: entorhinal cortex; DB: diagonal band of Broca; Am: amygdala; Hip: hippocampus; nST: nucleus stria terminalis; Fx: fornix; Cd: caudate nucleus; Pva: peri-third ventricle area; IT: inferotemporal cortex; PC: posterior cingulate cortex; RS: retrosplenial cortex. Orange arrow and crosses represent the injection coordinates. Dark blue clusters represent voxels with significant atrophy in the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortex. Light blue clusters represent voxels with significant tissue atrophy in the temporal areas of the brain (including the hippocampus, entorhinal cortex, amygdala, and lateral and inferior temporal cortices) as well as the diagonal band of Broca, fornix, and nucleus stria terminalis. Gray clusters represent other significant voxels. Maps derived from MRI recorded on n = 6 animals per group at 0, 3, 6, and 9 mpi and n = 6 and 4 animals in the Alzheimer- and control-inoculated groups, respectively, at 12, 15, and 18 mpi