Figure 5.
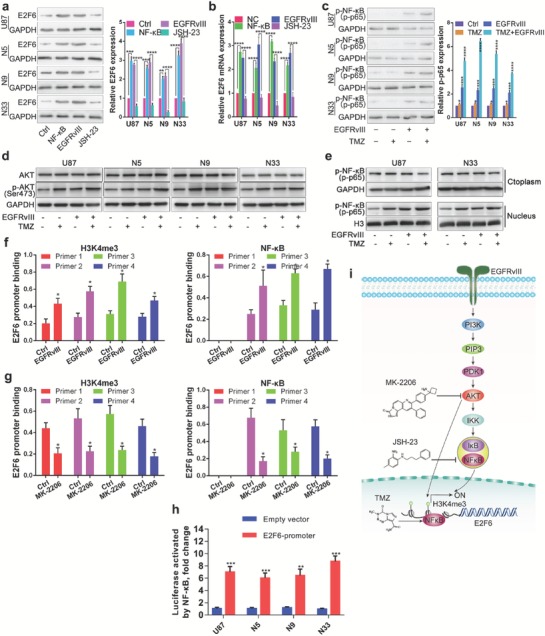
E2F6 is regulated by EGFRvIII/PI3K/AKT/NF‐κB and H3K4me3 modification. a) Western blot and b) qRT‐PCR analysis of E2F6 expression in GBM cells which were infected or treated with and without NF‐κB (p65/RelA), EGFRvIII, or JSH‐23. (mean ± SD, n = 3, ****P < 0.0001). c) Immunoblotting analysis of GBM cells with indicated antibodies after the cells were infected and treated with and without EGFRvIII and/or TMZ. p‐NF‐κB protein levels were quantified (right). (mean ± SD, n = 3, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). d) Western blot analysis of AKT and p‐AKT (Ser 473) with indicated treatment in four GBM cell lines. e) The cytoplasmic fraction and the nuclear fraction were separated for Western blot analysis of p‐ NF‐κB P65. f,g) ChIP‐PCR assay: EGFRvIII increased the enrichment of H3K4me3 and p‐NF‐κB in E2F6 promoter (d) whereas AKT inhibitor MK‐2206 treatment reduced the interaction of H3K4me3 and p‐NF‐κB to E2F6 promoter (e). (*P < 0.05). h) Four GBM cell lines were cotransfected with Renilla plasmid, NF‐κB (p65/RelA) plasmid, and reporter vectors containing cloned ChIP‐qPCR fragments of the E2F6 promoters. Luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla. (mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001). i) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of E2F6 regulation by the EGFRvIII/PI3K/AKT pathway. NF‐κB was simultaneously activated by EGFRvIII/PI3K/AKT and TMZ, leading to transcriptional activation of E2F6. In addition, the EGFRvIII/PI3K/AKT induced H3K4me3 modification which further activated E2F6 transcription.
