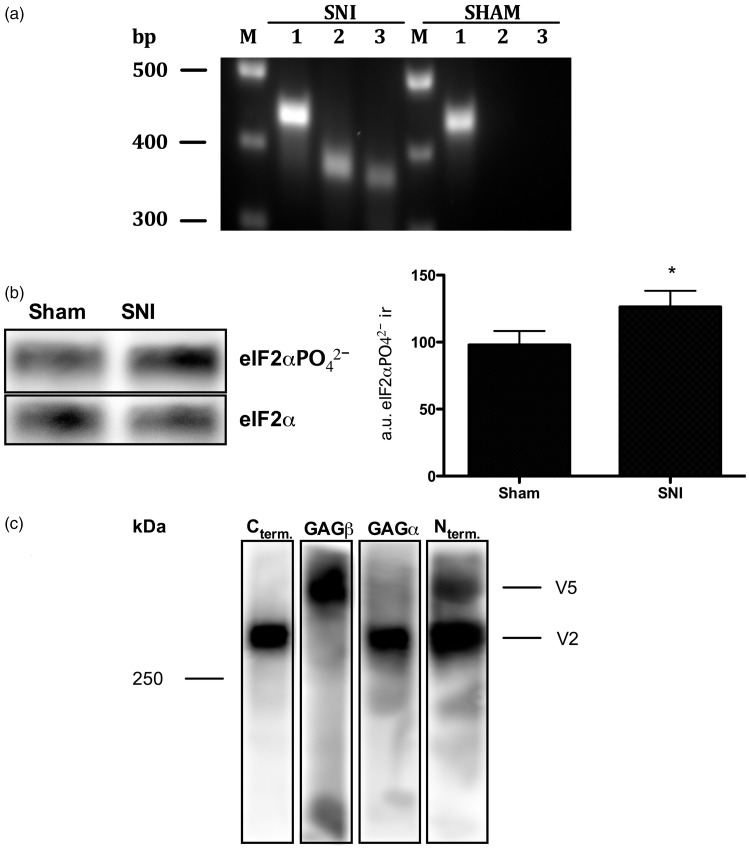
Figure 3.
A novel Vcan variant is expressed in SNI rats. (a) A novel Vcan variant is transcribed in SNI but not sham control rats. PCRs on cDNA from rat DRG demonstrates that the new Vcan variant is also transcribed in spared nerve injury rats but that it is absent in sham-operated rats. 1: Vcan_exon4_for and Vcan_exon6_rev = 435bp; 2: Vcan_exon8_for and Vcan_exon8β_rev = 372bp; 3: Vcan_exon8β_for and Vcan_exon11_rev = 360bp. (b) ISR is activated in SNI rats. Analyzing the post-translational modification of eIF2α by Western blotting demonstrates a significant increase of eIF2αPO42− in DRG extracts from rats submitted to SNI compared to sham-surgery rats [eIF2αPO42− immunoractivity in SNI = 126 ± 12 arbitrary units; eIF2αPO42− immunoractivity in sham controls = 98 ± 10 arbitrary units; normalized to the reference protein eIF2α; P<0.05 (unpaired student’s t-test), a 28.4 ± 15.8% increase in the eIF2αPO42− immunoreactivity, N=9]. Note that the calculated molecular weight of eIF2α ± PO42− is 36 kDa (according to the UniProtKB database entry P68101). *P<0.05. (c) SNI rats express a C-terminally truncated Vcan variant. DRG extracts from SNI rats were analyzed by Western blotting using a set of four different antibodies, each of which is directed against one of versican’s four major structural and functional domains. Rat V2 is made of 1601 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of ∼176 kDa.62 The discrepancy between its calculated and apparent molecular weight on the Western blot can be explained by its highly acidic character, which interferes with micelle formation during gel electrophoresis.63,64 The Vcan variant above V2 is composed of Vcan’s N-terminus and only the GAGβ domain. It’s domain composition and apparent molecular weight suggests that it is the C-terminal truncated Vcan variant predicted by the translation of V1-derived mRNAs carrying exon 8β.