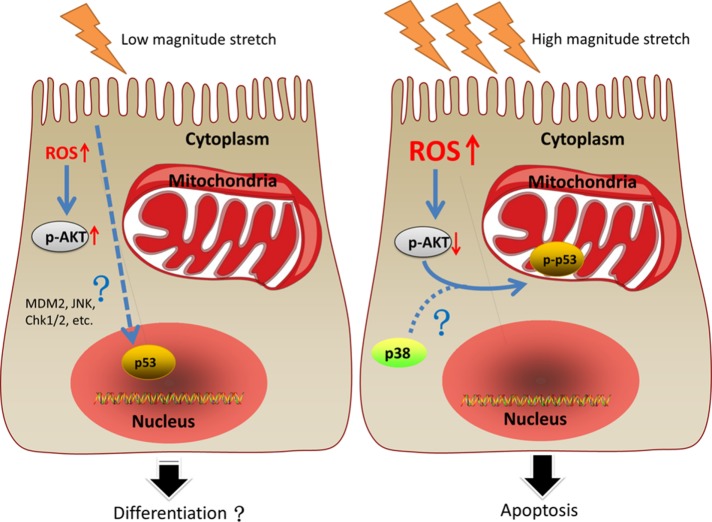
FIGURE 10:
An illustrative view of the different fates of C2C12 myoblasts under LMS or HMS stimulation. Left panel, LMS-induced mild elevation of ROS, resulting in the activation of AKT in C2C12 myoblasts. In addition, p53 was found in the nuclei of LMS-loaded C2C12 cells. Some studies demonstrated that lower magnitude cyclic stretch could promote myogenic differentiation, even though whether those changes in our study were related to C2C12 differentiation had not been explored. Right panel, HMS caused drastic apoptosis of C2C12 cells, which could be ascribed to the massive accumulation of ROS that dephosphorylated AKT. Inactivation of AKT in HMS-loaded C2C12 cells was shown to be necessary for p53 nuclear export in our study, a step required for its further phosphorylation on Ser389 that might involve p38 MAPK. Phospho-p53 (Ser389) translocated to mitochondria of C2C12 cells and induced their apoptosis under HMS stimuli.