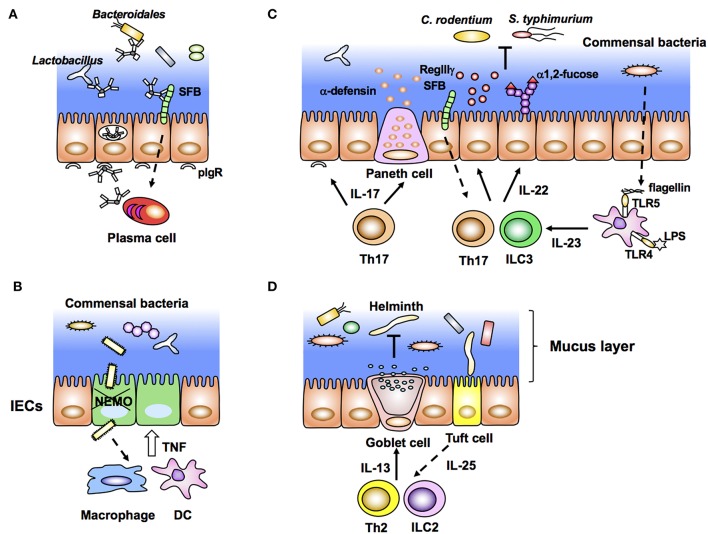
Figure 2.
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) stimulated by immune cells affect gut microbiota (inside-out signals). (A) Dimeric IgA antibodies produced by plasma cells in the lamina propria bind to pIgR expressed on the basolateral membrane of IECs, undergo transcytosis, and are secreted into the lumen as SigA. SIgA binds to commensal bacteria and maintains their homeostasis. (B) NEMO deficiency in IECs allows bacterial infiltration that leads to aberrant production of TNF from macrophages/DCs and further apoptosis of IECs. (C) Lamina propria DCs produce IL-23 in response to bacterial flagellin and LPS. IL-23 induces production of IL-22 from group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) and Th17 cells, leading to expression of epithelial anti-microbial molecules, such as RegIIIγ and α1,2-fucose. RegIIIγ and α1,2-fucose, which regulate the luminal microbial population. (D) Tuft cells produce IL-25 in response to helminth infection. Epithelial IL-25 promotes IL-13 production from ILC2 and Th2 cells, and subsequent production of mucus from goblet cells.