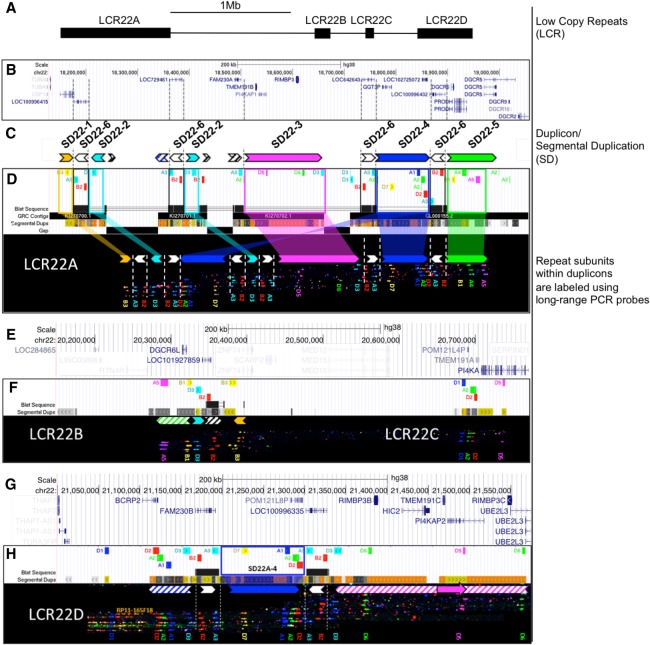
Figure 1.
In silico hg38 fiber FISH probe positions compared to duplicon composition of LCR22A. Terminology used to describe individual elements is depicted on the right. (A) Schematic overview of the LCR22s in Chromosome 22q11.21. (B) RefSeq-curated gene set overlapping with the LCR22s. (C) Duplicon decomposition of the hg38 structure of LCR22A. Duplicons were deduced from mapped haplotypes. Filled, colored arrows represent copies of duplicons and hatched arrows represent partial copies of duplicons of the same color. (D) UCSC Genome Browser hg38 reference assembly tracks of Segmental Dups2,24, GRC contigs, gap positions, and fiber FISH probe BLAT positions (white panel). Positions of the latter are aligned with recordings of fiber FISH patterns in LCR22A (black bar). Decomposition of one LCR22A haplotype to duplicons is illustrated using colored (nonwhite) arrows. For the showcased allele, duplicon order centromeric to telomeric is SD22-1, -2, -4, -2, -3, -4, and -5, and the arrow direction represents inverted or direct orientation. Larger duplicons are flanked by copies of SD22-6 (white arrows). Probe identifiers are indicated below the fiber pattern. (E) RefSeq annotated genes overlapping with LCR22B and -C. (F) LCR22B and -C, fiber FISH patterns have the same order and distances as those predicted in hg38 and contain partial duplication of LCR22A duplicons (hatched arrows). (G) RefSeq annotated genes overlapping with LCR22D. (H) All LCR22D molecules present at the same centromeric start, overlapping with predicted hg38 probe positions. The first duplicon displays a partial SD22-4 and SD22-2 (hatched blue arrow), followed by a complete SD22-4 flanked by SD22-6 copies (white arrow). The distal end of LCR22D consists of partial duplications of SD22-3 (hatched magenta arrow). Nested, solid magenta arrow represents probe D5 position variant.