FIGURE 5:
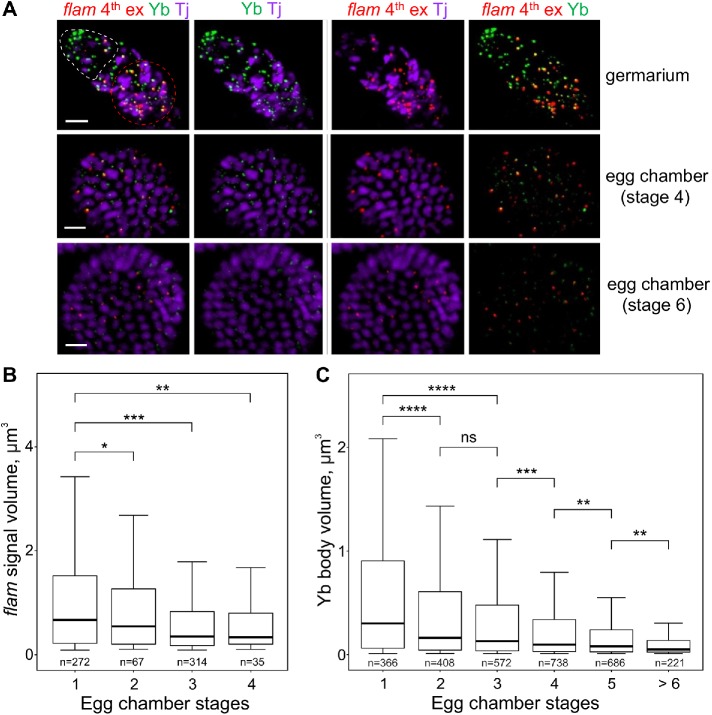
In ovarian follicle cells flam foci as well as the Yb bodies become progressively smaller during egg chamber maturation. (A) RNA FISH with flam fourth exon probe (red) in WT (flamKG/+) ovaries coupled with the immunostaining of Yb bodies by anti-Yb antibody (green) and anti-Tj antibody (violet), the nuclear marker of OSCs. Egg chambers at different stages in the same ovariole are shown. The apical region of a germarium is populated by cap and escort cells (outlined by a white dotted line), and the first stage follicle cells are located distally (outlined by a red dotted line). flam foci are most prominent in the first stage follicle cells of germaria (top panel) as well as in stage 2–3 egg chambers, whereas at the later stages of oogenesis (middle and bottom panels) flam as well as Yb body signals become weaker. Scale bars are 10 μm in the top panel and 7 μm in the middle and bottom panels. (B, C) Box plots showing a distribution of volumes of the flam fourth exon (B) or the Yb body (C) signals at different stages of egg chamber maturation in WT (flamKG/+) ovaries. Volumes of flam foci or Yb bodies from the indicated stages were measured with IMARIS software. The number of counted signals is indicated for each stage. M-W U-test was used for the pairwise comparison of distributions. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.