Figure 5. View of the CoQ-Binding Pocket and the Proposed Mechanism for Electron Transfer from Reduced FAD to DCQ.
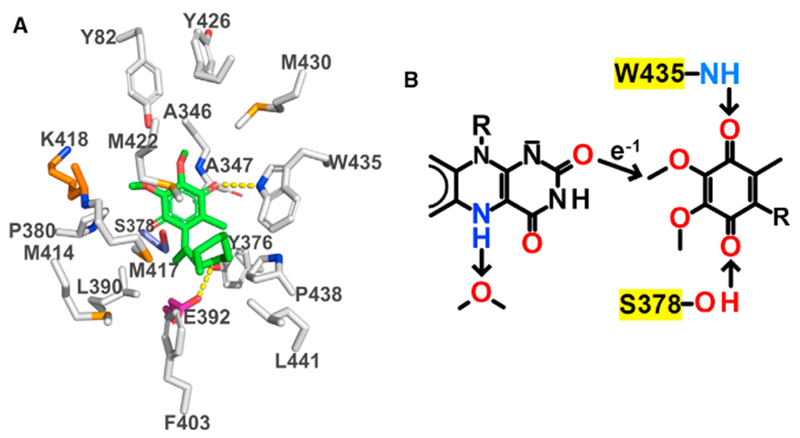
(A) Carbons in residues in the CoQ-binding pocket are colored according to residue type: nonpolar, white; negatively charged, magenta; positively charged, orange; polar, blue; carbons in DCQ are colored green. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed yellow lines.
(B) The arrow shows the single through-space jump from FAD:O2 to DCQ:C3M predicted by the program HARLEM. Trp435:NH1, Ser378:O, and a water molecule are proposed to act as proton donors or acceptors, as discussed in the text.
See also Figures 2A and 2B.
